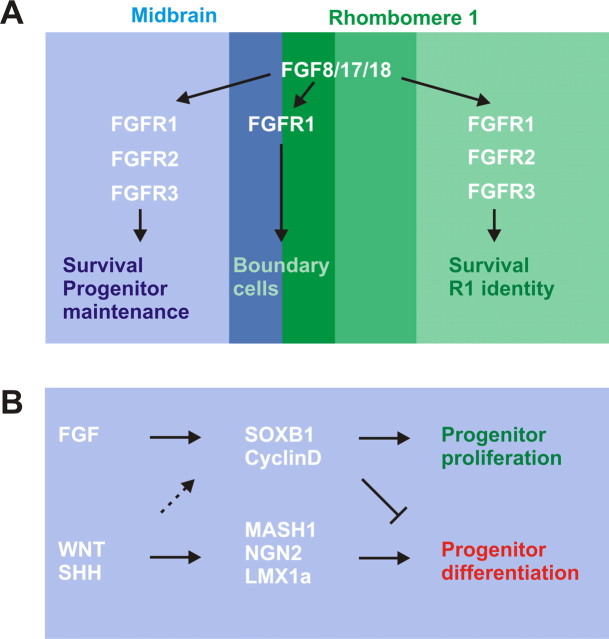
Figure 10.
Model of FGFR cooperation and signal integration regulating cell behaviors in the midbrain–rhombomere 1 region. A, Cooperation of FGFRs. FGF8 subfamily members secreted predominantly from the anterior r1 (dark green and medium green) act through three FGF receptors expressed in the midbrain–r1 region. FGFR1 is uniquely required for development of cell populations near the midbrain–r1 border. These include specialized boundary cells in the most posterior midbrain (dark blue) and most anterior r1 (dark green) as well as serotonergic neuron precursors of the dorsal raphe. Together with FGFR2 and, to a lesser extent, FGFR3, FGFR1 also supports cell survival, promotes r1 identity, and regulates the renewal of neural progenitor cells, including those of the midbrain DA neurons. B, Model of signal interactions regulating precursor cell characteristics in the ventral midbrain. FGFs, expressed posteriorly, support the self-renewing neural progenitor cell identity, possibly through SOXB1 and CyclinD family members. Ventral signals, including WNT and SHH, regulate DA neuron identity and neuronal differentiation involving LMX1 family transcription factor and proneural gene expression. Posteriorly, these signals may cooperate with the FGF pathway to support progenitor cell proliferation (dashed arrow).