Figure 2.
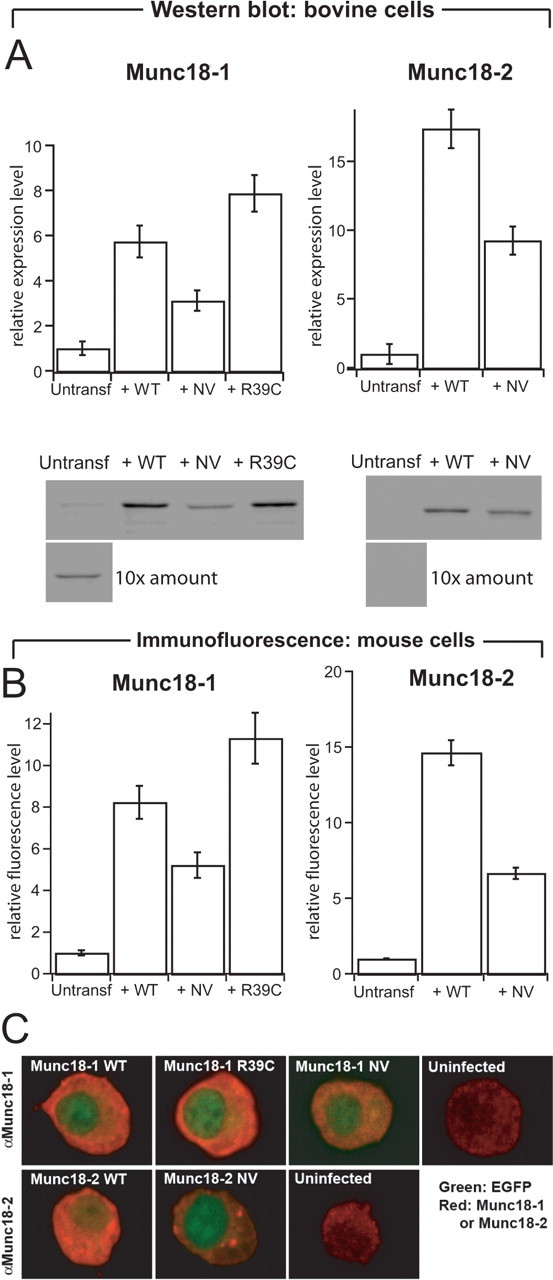
Protein levels of native and overexpressed Munc18 s in adrenal chromaffin cells. A, Quantification (top row) and representative Western blots (bottom row) stained for Munc18-1 (left column) or Munc18-2 (right column) from bovine cells (3 μg protein/lane). Cells were infected with SFV expressing the WT, NV, or R39C variant of Munc18s. For uninfected cells, 10 times the amount (30 μg protein/lane) was loaded to illustrate native Munc18 expression. The quantification of Munc18-1 and Munc18-2 protein levels was corrected for infected efficiency (40–80% of the cells were expressing the different constructs). n = 3 cell preparations. B, Quantification of protein levels from expressing and untransfected embryonic mouse chromaffin cells (munc18-1 +/+) using immunofluorescence. The NV mutations were expressed at half the level of wild-type proteins. Data are mean ± SEM from 29–51 cells. C, Confocal sections through the equatorial plane of embryonic mouse chromaffin cells (munc18-1 +/+) immunostained for Munc18-1 (top row) or Munc18-2 (bottom row) and expressing the constructs indicated. Red, Munc18-specific staining; green, EGFP fluorescence. EGFP was expressed from the same viral constructs as a separate protein and found throughout the cell but is visible here mainly in the nucleus because of the intense cytoplasmic Munc18 staining. Munc18-1 and Munc18-2 were found throughout the cytoplasm, as expected. In addition, in some but not all cells, Munc18-2 NV was found concentrated in spots within the cytosol. Refer also to Figure 3, which shows that all variants were present on plasma membrane sheets. Note that the confocal sections were taken with different photomultiplier settings to visualize the distribution and therefore do not yield quantitative information about expression levels. Quantitative information is present in A and B.
