Figure 9.
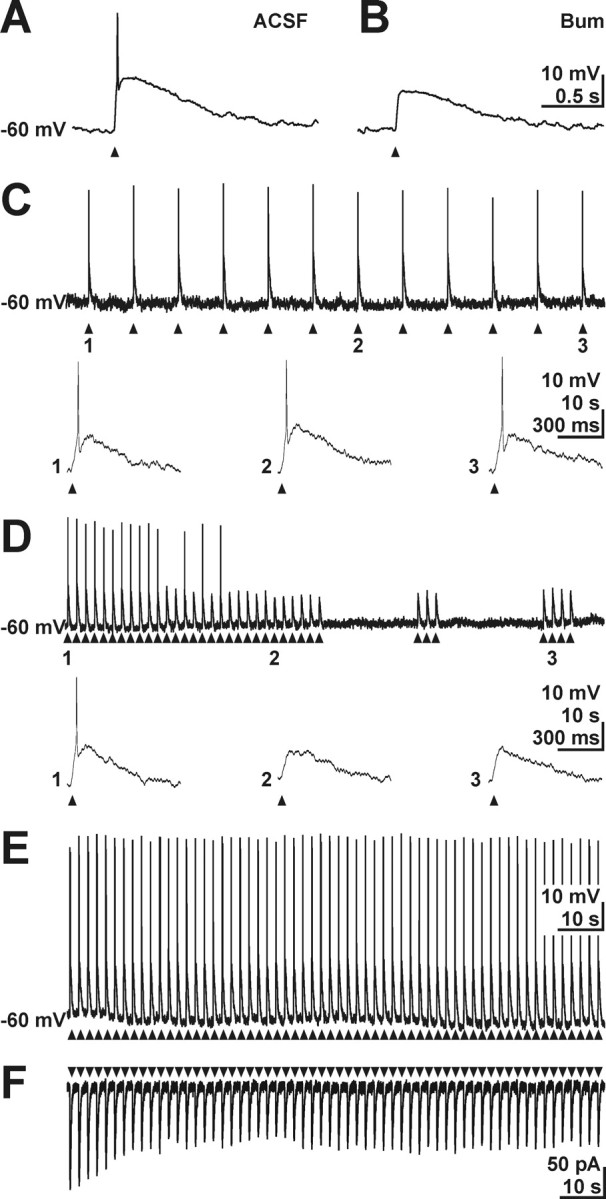
Effect of active Cl− uptake on GABA responses in CR cells. A, Gramicidin-perforated patch-clamp recording of a CR cell. Focal GABA application (arrowheads) elicited APs. B, In the same cell, 50 μm bumetanide suppressed GABA-induced AP. C, Repetitive GABA pulses (arrowheads) at a frequency of 0.1 Hz reliably elicited APs at each application under perforated-patch conditions. Events indicated by numbers are shown at a larger time scale below the current trace. D, Subsequent increase in application frequency to 0.5 Hz attenuated the amplitude of GABA responses and abolished AP (2). The amplitude of GABA-induced depolarization increased slightly after cessation of repetitive application, but no AP could be elicited (3). E, Current-clamp recording of GABA responses under whole-cell conditions at a [Cl−]p of 30 mm. Under whole-cell conditions, GABA application at a frequency to 0.5 Hz reliably evoked APs. F, Voltage-clamp recording of GABA responses under whole-cell conditions at a [Cl−]p of 30 mm. Repetitive application at a frequency to 0.5 Hz led to a partial desensitization of GABAergic inward currents.
