Figure 2.
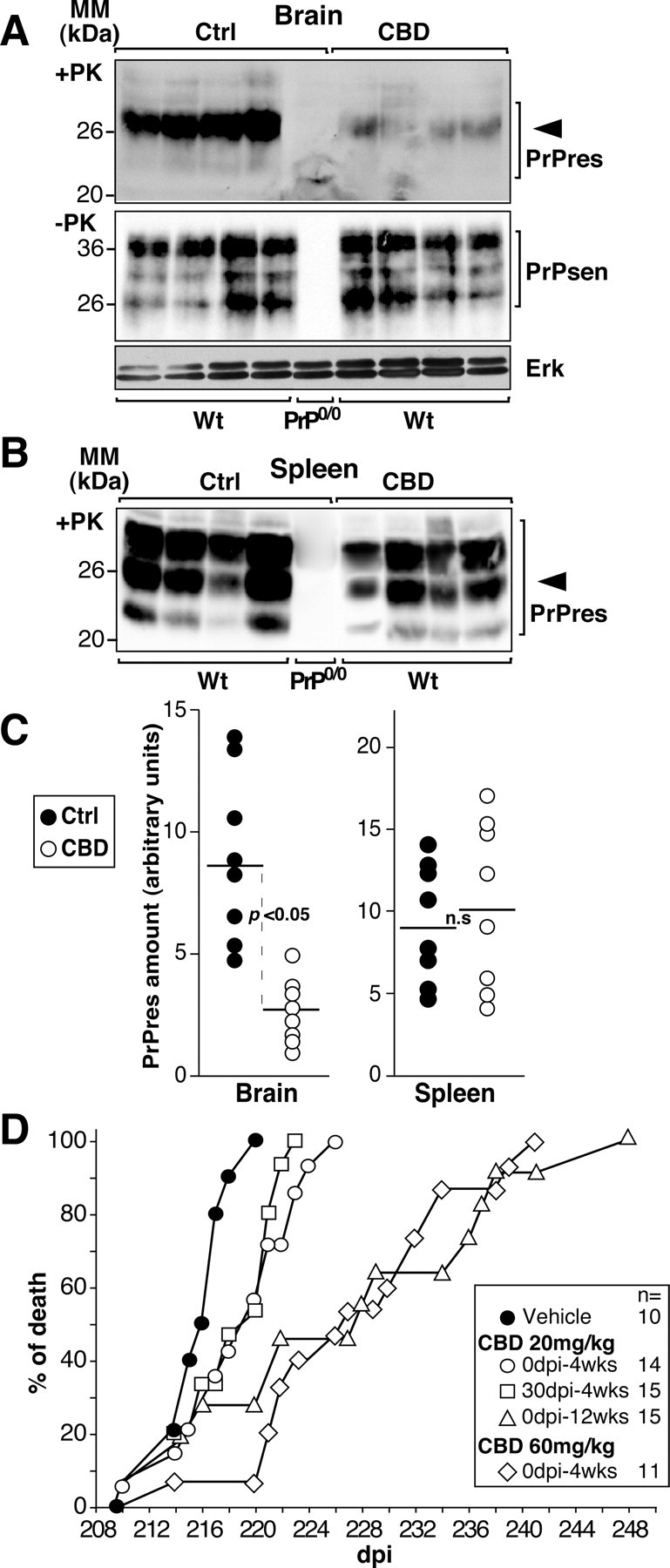
CBD prevents cerebral PrPres formation and prolongs prion disease incubation time in scrapie strain-infected mice. A, B, Western blot analyses performed on brain (A) or spleen (B) homogenates of scrapie-infected C57BL/6 wild-type (Wt) or PrP0/0 mice treated three times per week intraperitoneally for 3 weeks with 20 mg/kg CBD; the control (Ctrl) group of animals (n = 8) was treated with the vehicle alone. The treatments began the day of scrapie infection. Forty days after infection, mice were killed, and tissues were homogenized in lysis buffer. Detection of PrPsen or Erk (A, middle and bottom) and PrPres (A, top, B) were performed on undigested and PK-treated lysates, respectively. Four hundred micrograms (A, top, B) and 25 μg (A, middle and bottom) of total proteins were loaded per lane. Densitometry analysis was performed on the band indicated by the arrowhead, and the amount of PrP was calculated as follows: mean intensity/surface × correction factor for load as expressed in arbitrary units. MM, Molecular mass. C, Each dot represents the normalized PrPres content of a single vehicle-treated (Ctrl; ●) or CBD-treated (○) wild-type mouse. The dark line is the mean value. D, Days to death of infected C57BL/6 mice treated with the vehicle alone (●) or with CBD at the indicated concentration (open symbols). The starting point in days postinfection (dpi) and the duration of the treatment in weeks (wks) are indicated. Individual data points represent the percentage of dead mice out of the total number of mice infected for each group. Multiple mice may be represented by a single data point. The legend is shown on the right, and the number of mice is indicated. Significance (p) was evaluated using the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Differences were considered significant for p values <0.05. n.s., Not significant.
