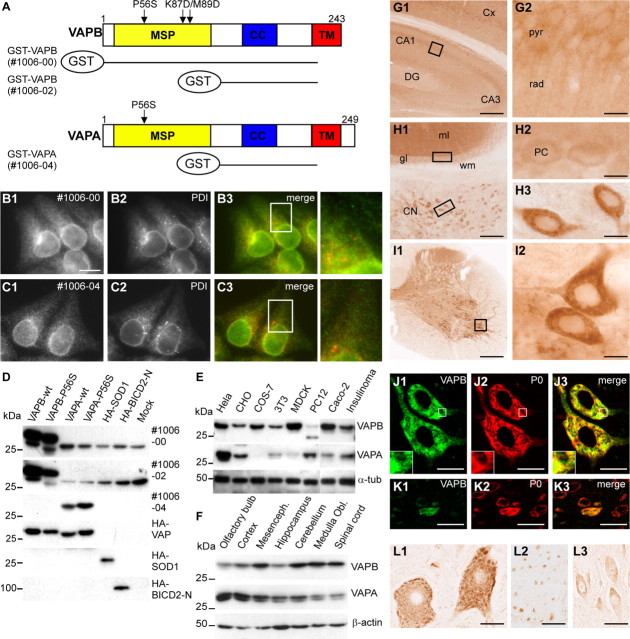
Figure 1.
Distribution and localization of VAPB in vivo. A, Antisera against VAPA and VAPB were made against GST-VAP fusion proteins containing amino acids 1–225 of VAPB (antibody #1006-00) and amino acids 132–225 of VAPA (#1006-04) and VAPB (#1006-02). cc, Coiled-coil region; TM, transmembrane domain. B, C, Cells were fixed and processed for immunofluorescence using antibodies to VAP (green) and PDI (red). D–F, Lysates of COS-1 cells expressing VAP and control proteins (D), cultured cells (E), and mouse CNS (F) were analyzed by immunoblotting using VAP antibodies. G–I, Low- (G1, H1, I1) and high-magnification (G2, H2, H3, I2) of immunoperoxidase stainings using anti-VAPB antibody #1006-00 in murine dorsal hippocampus (G), cerebellum (H), and spinal cord (I). VAPB is expressed at high levels in motor neurons (I2) and large neurons in the cerebellar nuclei (CN; H1, H3) compared with neurons in cerebellar cortex (H1) including cerebellar Purkinje cells (PCs; H2) and hippocampus (G), including hippocampal pyramidal cells (G2). DG, Dentate gyrus; pyr, pyramidal layer; rad, stratum radiatum of CA1 hippocampal subfield; gl, granule-cell layer; ml, molecular layer; wm, white matter. J, K, Double-labeling confocal immunofluorescence of VAPB immunoreactivity (green) and ribosomal protein P0 (red) in mouse spinal motor neurons (J) and dorsal horn neurons (K). VAPB (J1, K1) colocalizes with P0 (J2, K3) in motor neurons, but shows low expression levels in most dorsal horn neurons. A merge is shown on the right. L, Immunoperoxidase staining using anti-VAPB antibody #1006-00 in human lumbar motor neurons (L1), ventral root motor axons (L2), and CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons (L3). As in mouse, in human VAPB-immunoreactivity in motor neurons is considerably higher than in other neurons, showing a Nissl body-like distribution (L1). Scale bars: G1, I1, 200 μm; H1, 100 μm; G2, H2, H3, I2, 10 μm; J3, K3, 20 μm; L1, L2, L3, 30 μm.