Figure 7.
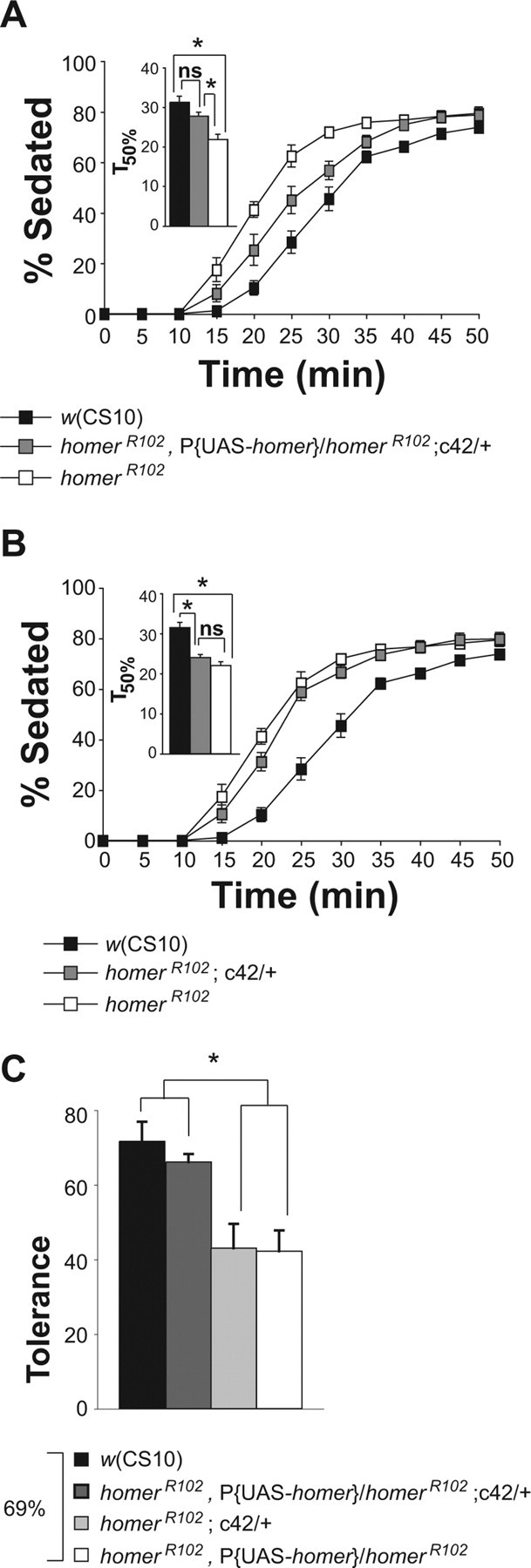
Spatially restricted expression of Homer in the brain with c42-GAL4 rescued sensitivity and rapid tolerance. A, Expression of P{UAS-homer-myc} by the c42-GAL4 driver rescued the homerR102 ethanol sensitivity phenotype. The T50% of the homerR102 flies was significantly different from the T50% of the w(CS10) and homerR102,P{UAS-homer}/homerR102;c42-GAL4 flies as measured by a one-factor ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni/Dunn comparisons (n = 7; *p < 0.0167). B, Mutant homerR102 flies carrying the c42-GAL4 driver alone showed ethanol sensitivity indistinguishable from homerR102 mutant flies. The T50% of the homerR102 flies was not significantly different from the T50% of the c42-GAL4; homerR102 flies as measured by a one-factor ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni/Dunn comparisons (n = 7; *p < 0.0167). C, The expression of P{UAS-homer-myc} by the c42-GAL4 driver rescued the homerR102 rapid tolerance phenotype to w(CS10) control levels. The asterisk indicates significant differences as determined by a one-factor ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni/Dunn comparisons (n = 5; *p < 0.0083). Error bars indicate SEM. ns, Not significant.
