Figure 6.
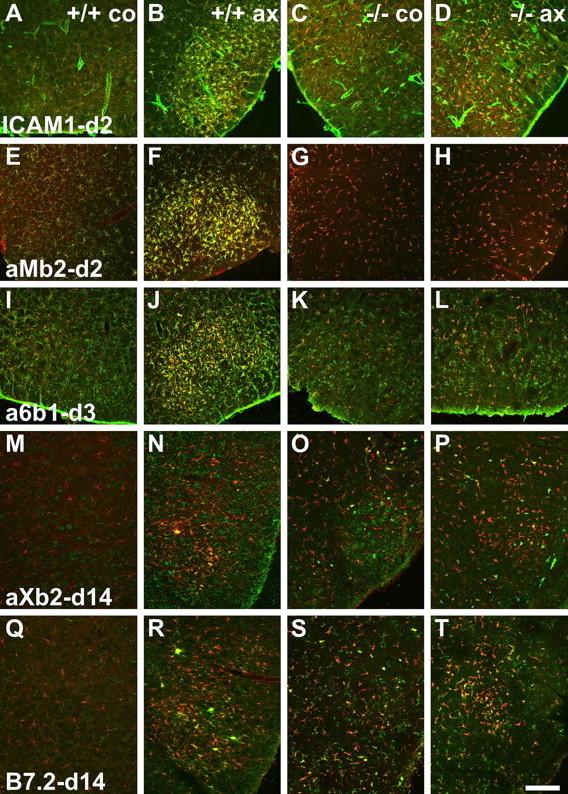
TGFβ1−/− deficiency causes a split response in the regulation of early (ICAM1 and αMβ2 integrin), midphase (α6β1), and phagocytic (αXβ2 and B7.2) markers on microglia after facial axotomy (ax) and on the contralateral side (co). Double immunofluorescence is shown with microglial IBA1 counterstaining in red and other labels in green. A–L, In the first group, absence of TGFβ1 interferes with the upregulation of ICAM1 (A–D), αMβ2 integrin (E–H), and α6β1 (I–L), normally observed at days 2 and 3 in the TGF β1+/+ mice. M–T, In the second group, small αXβ2- (M–P) and B7.2-(Q–T) immunoreactive microglia are already present in the contralateral facial motor nuclei in the TGFβ1−/− mice; their numbers are barely affected by facial axotomy. In control, TGF β1+/+ animals, facial axotomy normally leads to the appearance of large, αXβ2- and B7.2-immunoreactive microglial nodules, peaking at day 14, that remove dead neuronal debris. Scale bar: (in T) A–L, 250 μm; M–T, 330 μm.
