Figure 2.
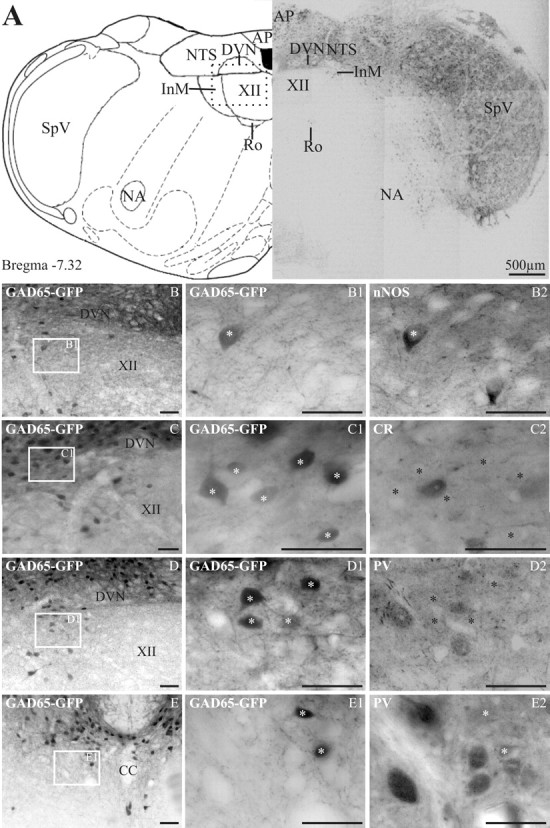
In GAD65–GFP tissue, GFP-expressing neurons are found in many dorsal medullary structures. In the InM, GFP is preferentially found in neurons expressing nNOS. A, The left panel is an orientation diagram showing the location of various nuclei at the level represented by the low-power montage of GFP-expressing neurons illustrated in the right panel. The boxed area represents the approximate region of the micrographs in B–D. AP, Area postrema; Ro, nucleus of Roller; SpV, spinal trigeminal; NA, nucleus accumbens. B–D, Low-power images showing the location of GFP-expressing neurons within the InM. The boxed area in each image is shown at a higher magnification in B1–D1, respectively. B2, nNOS immunoreactivity within the same region as B1, showing one GAD65–GFP-positive and one GAD65–GFP-negative neuron. C2, CR immunoreactivity on the same section of medulla; no neurons with CR immunoreactivity also express GFP. D2, PV immunoreactivity within the same region showing no colocalization between PV and GFP. E, A low-power image of the CCN showing the location of GFP-expressing neurons. E1, A more magnified image of the area indicated in E. E2, PV-immunoreactive neurons within the CCN are GFP negative and are located ventral to GFP neurons. The asterisks in B2–E2 indicate the location of GFP-positive neurons visible in respective panels B1–E1. Scale bars: B–E2, 50 μm. CC, Central canal.
