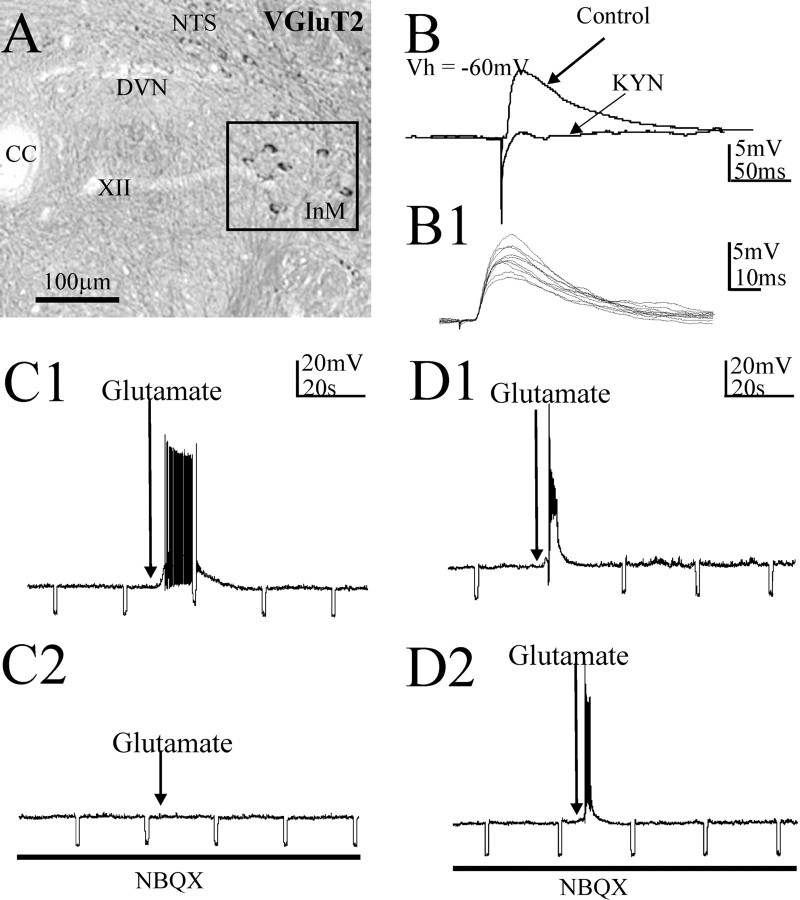
Figure 6.
Monosynaptic excitatory projections from the InM to the NTS in the rat revealed electrophysiologically are reflected by VGluT2 expression in InM neurons. A, In situ hybridization studies localized neurons within the InM positive for a VGluT2 mRNA probe. The boxed area highlights the InM. B, An example of an EPSP in an NTS neuron at a holding potential of −60 mV, evoked by electrical stimulation of the InM. Application of 1 mm kynurenic acid (KYN) blocked this EPSP. B1, Example of 10 consecutive EPSPs recorded from a NTS cell highlighting the minimal synaptic jitter in the excitatory pathway between the InM and NTS. C1, C2, A depolarization elicited in an NTS neuron by local microinjection of 40 mm glutamate in the InM (C1). This response was blocked by bath application of 10–20 μm NBQX (C2). D1, D2, Local microinjection of glutamate overcomes EAA blockade by bath-applied antagonists. In this example, action potentials within an InM neuron from a holding potential of −60 mV were observed in response to local microinjection of 40 mm glutamate in the InM (D1). This response was not blocked by bath application of NBQX (D2). CC, Central canal.