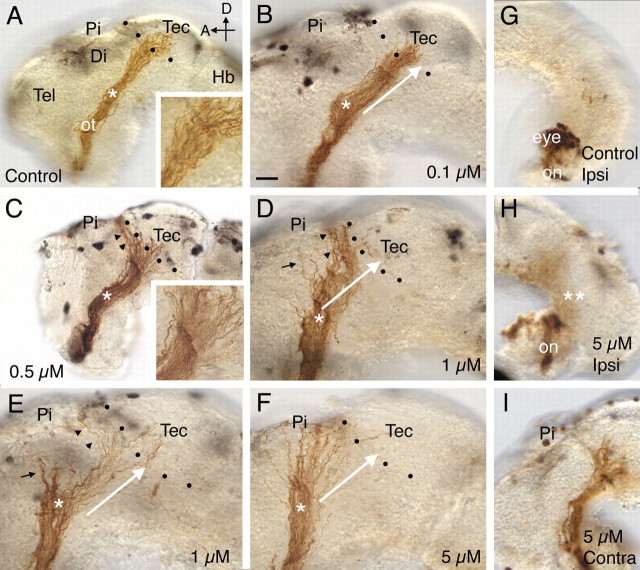
Figure 2.
A–I, Pharmacological inhibition of ADAM10 causes defects in target recognition. HRP-labeled optic projections in stage 40 brains exposed at stages 31 or 33/34 to either a control solution (A, G) or a solution containing the ADAM10 inhibitor, GI254023X (B–F, H, I) are shown. Dotted lines show the approximate anterior border of the optic tectum. A, Control DMSO solution. Axons grow through the diencephalon, make a turn in the mid-diencephalon (asterisk), and innervate the optic tectum. The inset shows the behavior of axons at the border of the optic tectum. B, GI254023X (0.1 μm). The white arrow indicates the normal trajectory of RGC axons after the mid-diencephalic turn (asterisk) and has been included in D–F for comparison purposes. C, GI254023X (0.5 μm). Many RGC axons fail to recognize their target and turn and grow along the anterior border of the optic tectum (black arrowheads). The inset shows a high-power view of the optic projection at the border of the optic tectum. D, E, GI254023X (1 μm). Some axons fail to recognize the optic tectum (black arrowheads) or make an earlier guidance error at the mid-diencephalic turn (black arrows). F, GI254023X (5 μm). Most axons fail to turn in the mid-diencephalon (asterisk; compare trajectory of axons to that of the white arrow) and never reach the anterior border of the optic tectum. G–I, HRP-labeled RGC axons in stage 39 brains where only the optic chiasm was exposed at stage 31 to either a control solution (G) or a solution containing 5 μm GI254023X (H, I). In the G1254023X-treated brain (H), as in control (G), there is no obvious ipsilateral projection, and the optic nerve crosses over at the optic chiasm to the contralateral side of the brain and grows normally within the diencephalon that is not exposed to the inhibitor (I). Tec, Tectum; Pi, pineal gland; ot, optic tract; Di, diencephalon; Hb, hindbrain; on, optic nerve; Ipsi, ipsilateral; Contra, contralateral; D, dorsal; A, anterior; Tel, telencephalon. Scale bar: (in B) A, C, G–I, 50 μm; B, D–F, 30 μm.