Figure 6.
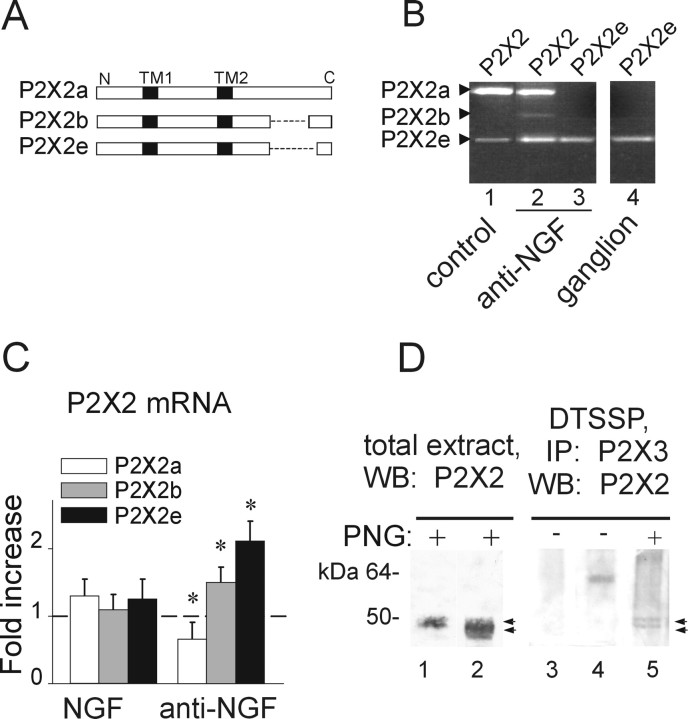
Anti-NGF treatment differentially affects the expression of P2X2 subunit splice variants. A, Schematic representation of different P2X2 splicing forms. P2X2b or P2X2e splice variants lack 69 (from Val383 to Gln451) or 90 (Val383 to Gln472) amino acids, respectively (dashed line) in the C-terminal intracellular domain. Transmembrane regions (TM1 and TM2) are represented in black. B, Photographs of ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel electrophoresis of end-point RT-PCR experiments show the presence of P2X2 splicing forms in TG cultures grown in control conditions (lane 1) or after anti-NGF treatment (lane 2). Primers selective for the P2X2e amplify only this splicing variant in cultures treated with anti-NGF (lane 3) as well as in TG tissue (ganglion, lane 4). Amplicons show the expected length: 686, 479, and 416 bp (for P2X2a, P2X2b, and P2X2e, respectively). C, Quantitative real-time RT-PCR experiments performed with P2X2 splicing-specific primers. Anti-NGF antibody treatment upregulates P2X2b and P2X2e mRNA levels (n = 3; *p = 0.04 and *p = 0.02, respectively), although it proportionally reduces P2X2a (n = 3; *p = 0.04). Chronic NGF treatment has no effect (left histograms). Samples are normalized with respect to mRNA levels in control condition (dashed line). D, Deglycosylation experiment of P2X2 subunit in total extract of TG cultures in control or after anti-NGF treatment (lanes 1, 2; n = 4). The same protocol is also applied to P2X2/3 receptors immunopurified from anti-NGF-treated cells (lane 5; n = 2). Lane 3 shows untreated culture extract without PNGaseF application; lane 4 shows single band (P2X2/3 receptor) without PNGaseF treatment from culture after anti-NGF. Note that PNGaseF deglycosylation (PNG) is required to recognize discrete double bands (with apparent molecular weight of 50 and 45 kDa, respectively; lanes 2 and 5, arrows) relative to P2X2 differentially spliced polypeptides. IP, Immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot.