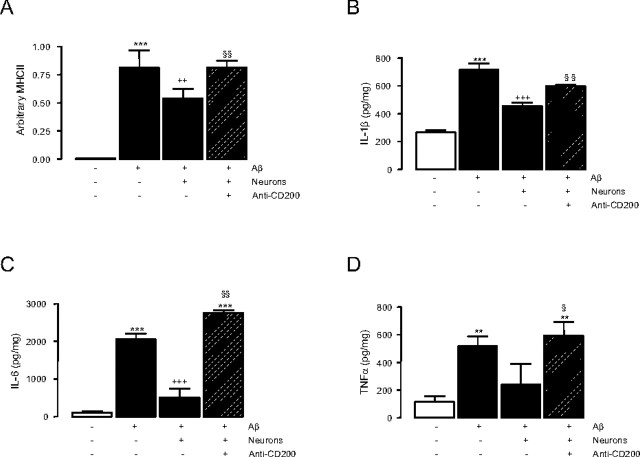
Figure 3.
Blocking CD200–CD200R interaction reverses Aβ-induced glial cell activation. A–D, Aβ significantly increases MHCII mRNA expression (A; n = 4; one-way ANOVA, ***p < 0.001) and IL-1β (B; n = 8; one-way ANOVA, ***p < 0.001), IL-6 (C; n = 4; one-way ANOVA, ***p < 0.001), and TNFα (D; n = 4; one-way ANOVA, **p < 0.01) release in glial cell cultures, and this is attenuated by the addition of neurons (MHCII, ++p < 0.01; IL-1β, +++p < 0.001; IL-6, +++p < 0.001). The addition of anti-CD200 antibody in the presence of neurons significantly abrogates the effect of neurons alone (MHCII, §§p < 0.01; IL-1β, §§p < 0.01; IL-6, §§p < 0.01; TNFα, §p < 0.05). Error bars indicate ±SEM.