Figure 4.
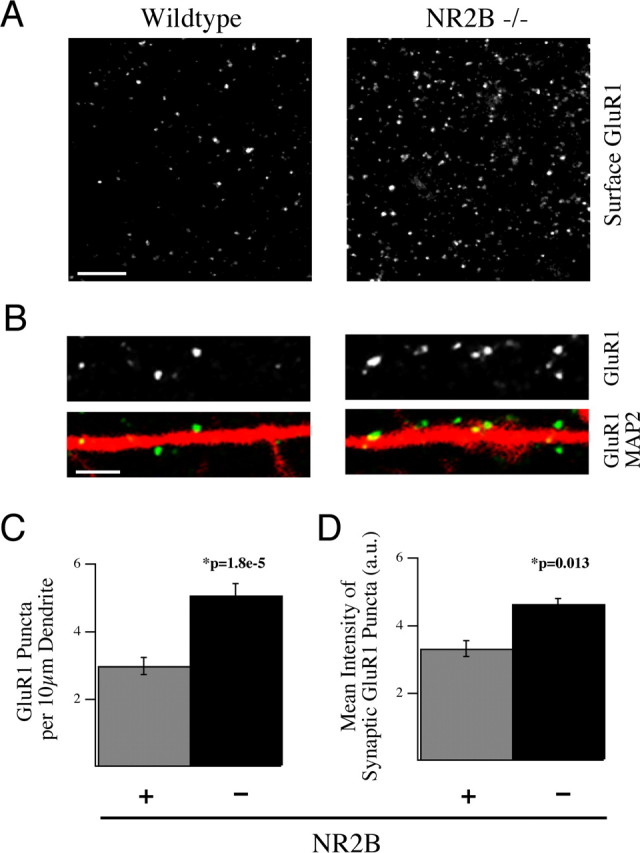
NR2B negatively regulates surface and synaptic localization of the AMPAR subunit GluR1. A, B, Cultured cortical neurons from NR2B−/− embryos (right) and WT littermates (left) were live labeled with anti-GluR1 antibodies and subsequently fixed and stained for MAP2 at 14 DIV. These data show the dramatic increase in surface localization of this receptor subunit in the absence of NR2B. Scale bars; A, 5 μm; B, 2 μm. C, D, Cultures at 14 DIV were live labeled for GluR1 and then fixed and stained for MAP2 and the synaptic marker VGlut1 and VGlut2. C, Quantification of the immunostaining data showing the surface expression of GluR1 puncta per length of dendrite was increased in NR2B−/− neurons compared with WT neurons. D, The integrated pixel density of GluR1 staining in VGlut1- and VGlut2-positive synapses was also significantly increased in NR2B−/− neurons versus control neurons (350 synapses per animal). All histograms show mean ± SEM.
