Figure 1.
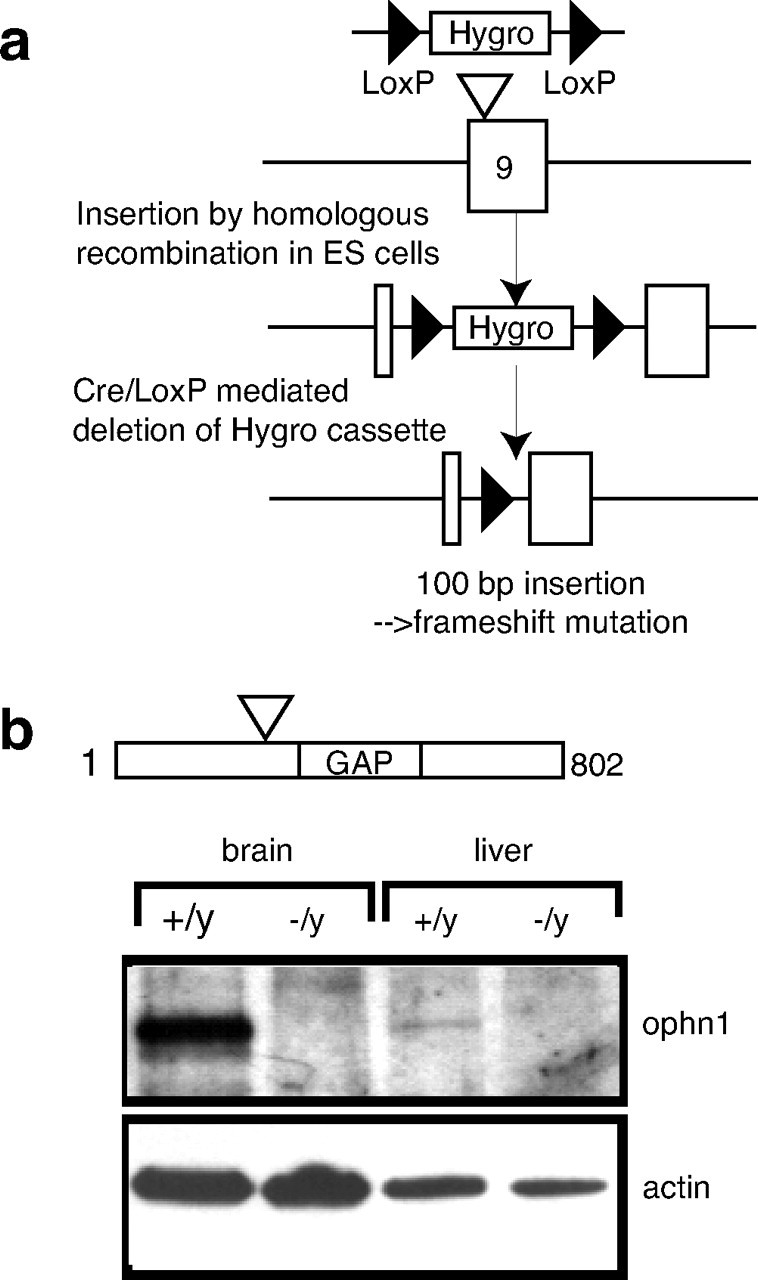
Ophn1 gene inactivation. a, Strategy of mouse ophn1 inactivation gene. The strategy was designed to disrupt the open reading frame of the ophn1 gene by the insertion of 100 bp in the coding sequence of exon 9, which leads to the premature STOP codon after the BAR domain (amino acids 1–242) and before the PH and GAP domains. Exon 9 was targeted by homologous recombination leading to the insertion of a phosphoglycerolkinase-hygromycin-resistant gene cassette (Hygro) flanked with LoxP sites. The Cre recombinase catalyzed the deletion of sequences between LoxP sites and led to the removal of the selective cassette in the final ophn1-mutated allele. b, Western blot analysis of brain and liver lysates from ophn1+/y and ophn1−/y adult mice. Rabbit polyclonal antibodies recognizing both ends of ophn1 protein demonstrated the absence of full-length ophn1 protein (91 kDa) or truncated products (data not shown) in ophn1−/y. Anti-actin antibody was used as a loading control.
