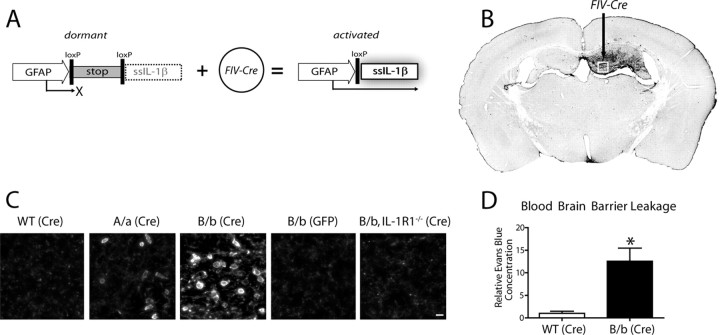
Figure 1.
Activation of a transcriptionally silent hIL-1β transgene within the hippocampus drives leukocyte recruitment. Adult IL-1βXAT mice received intrahippocampal injections of either FIV-Cre or FIV-GFP control virus unilaterally. A, Structure of the dormant IL-1βXAT transgene and subsequent conversion to an activated state after exposure to FIV-Cre. B, A coronal section from an IL-1βXAT line B/b mouse 2 weeks after FIV-Cre injection (black arrow) into the dentate gyrus demonstrates spatially restricted CD45 staining in the ipsilateral (right) hemisphere. C, CD45 staining of leukocytes was performed in parallel groups of animals within the ipsilateral dentate gyrus represented by the white box in B. Representative images were captured from WT, IL-1βXAT line A/a (A/a), IL-1βXAT line B/b (B/b), and IL-1βXAT line B/b animals lacking IL-1R1 (B/b, IL-1R1−/−) injected with FIV encoding the protein designated in parentheses. Background CD45 staining reflects low-affinity binding to microglia within the hippocampus (scale bar, 10 μm). D, Hippocampal BBB leakage, as evidenced by Evans Blue concentration, in IL-1βXAT line B/b versus WT animals 2 weeks after transgene activation. Graph represents mean ± SEM. n = 3 animals per group. *p ≤ 0.05.