Figure 4.
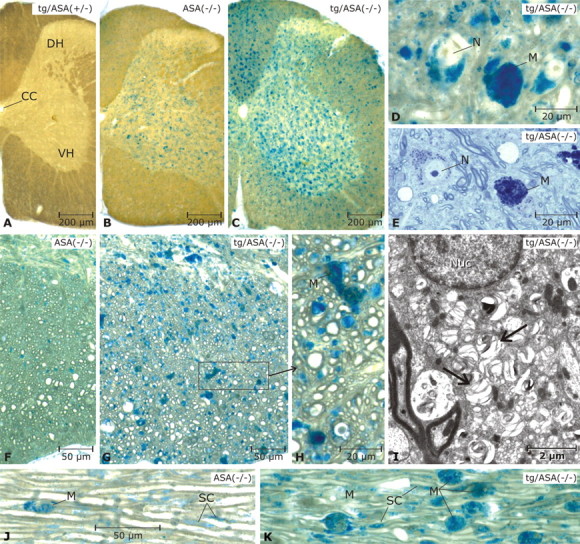
Sulfolipid storage in spinal cord and peripheral nerve. Vibratome slices of 17-month-old mice were incubated with alcian blue to detect sulfoglycolipds. Mice were from the transgenic line tg2645. A, In the tg/ASA(+/−) spinal cord, no alcianophilic material is seen. B, In the non-tg ASA(−/−) spinal cord, alcianophilic material is seen mainly in the gray matter, where it is contained in neurons and micoglia/macrophages (details not shown). C, In the tg/ASA(−/−) spinal cord, the frequency of alcianophilic structures is increased. This is related mainly to increased numbers of sulfolipid-storing microglia/macrophages in the gray matter as well as the white matter. D, E, Details of the gray matter in the tg/ASA(−/−) spinal cord (D, paraffin section, pre-embedding incubation with alcian blue; E, semithin section, stained with toluidine blue). Storage in neurons and macrophages is evident. F–H, Details in the white matter shown in paraffin sections (pre-embedding incubation with alcian blue as in D). In the non-tg ASA(−/−) mouse (F), the alcianophilic material detected in this type of preparation is rather scarce, whereas in the tg/ASA(−/−) mouse (G), many small and some large alcianophilic profiles are seen. The latter correspond to macrophages (M) as shown in H (enlarged area marked in G), whereas most of the numerous small profiles correspond to oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocytic processes. I, The ultrastructure of an oligodendrocyte; the cytoplasm contains numerous lamellated inclusions of low electron density (arrows). Nuc, Nucleus. J, K, Trigeminal nerves (paraffin sections, pre-embedding incubation with alcian blue as in D). Alcianophilic material is seen in macrophages and Schwann cells (SC). Scale bars: A–C, 200 μm; D, E, H, 20 μm; F, G, J, K, 50 μm; I, 2 μm. CC, Corpus callosum; DH, dorsal horn; VH, ventral horn; N, neurons; M, macrophages.
