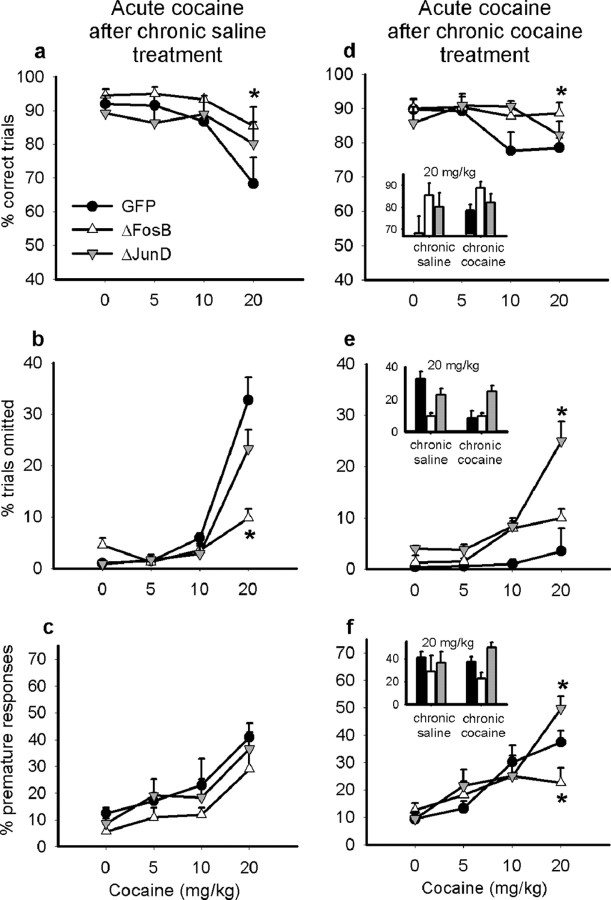
Figure 6.
Effects of an acute cocaine challenge on 5CSRT performance after previous chronic treatment with saline or cocaine. The effects of an acute cocaine challenge on task performance were not altered by previous chronic treatment with saline. Animals were less accurate (a) and made more omissions (b), effects that were attenuated in animals overexpressing ΔFosB. All animals continued to make more premature responses (c). After chronic cocaine treatment, an acute cocaine challenge impaired accuracy in all animals other than those overexpressing ΔFosB (d). However, control (GFP expressing) animals treated chronically with cocaine made fewer omissions when subsequently challenged with cocaine on task (e). This effect was mimicked by overexpressing ΔFosB and blocked by overexpressing ΔJunD (e.g., at 20 mg/kg, inset graph). After chronic cocaine treatment, the acute cocaine-induced increase in premature responding was reduced in animals overexpressing ΔFosB but augmented in animals overexpressing ΔJunD (f; e.g., at 20 mg/kg, inset graph). Data shown are mean + SEM. *p < 0.05.