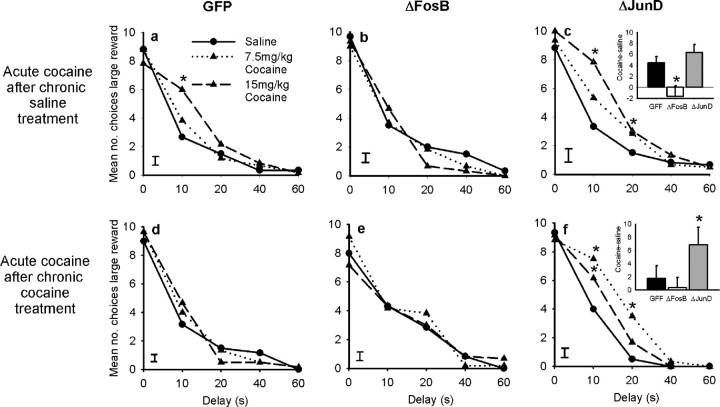
Figure 7.
Effects of an acute cocaine challenge on delay-discounting performance after previous chronic treatment with saline or cocaine. The effects of an acute cocaine challenge on task performance were not significantly altered by previous chronic treatment with saline. Cocaine lead to a significant increase in choice of the larger delayed reward in both control (GFP expressing) animals (a) and animals overexpressing ΔJunD (c) but not in animals overexpressing ΔFosB (b). After chronic treatment with cocaine, an acute cocaine challenge no longer altered impulsive decision making in control animals (d) or in animals overexpressing ΔFosB (e). Animals overexpressing ΔJunD did not develop any tolerance to the effects of cocaine (f). Data shown are mean + SEM. To summarize these data, the inset graphs in c and f show the total number of choices of the large reward after cocaine (15 mg/kg) minus that observed after saline administration. Data shown are mean + SEM. *p < 0.05.