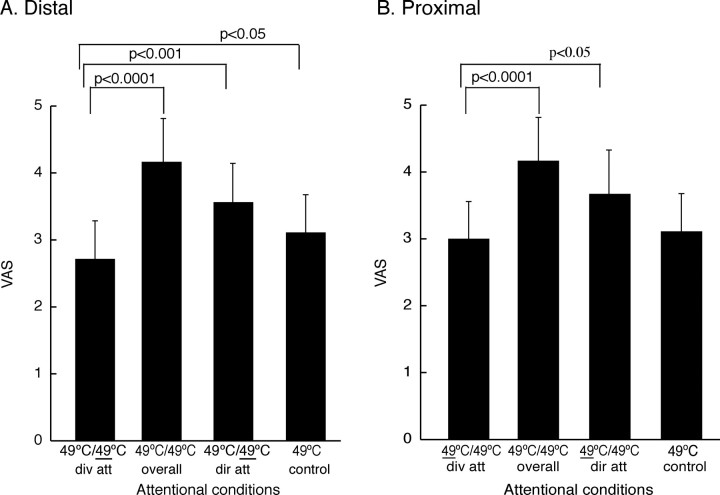
Figure 2.
Attention modulates spatial integration of information from two noxious stimuli (mean ± SEM). A, B, During divided attention (div att; 49/49°C and 49/49°C) spatial summation of pain (49/49°C overall) was abolished at distal (49/49°C div att; A) and proximal sites (49/49°C div att; B). This was associated with inhibition when compared with a single 49°C (49 control) at distal stimuli (A) but not at proximal sites (B). The modulation of pain was not attributable to nonspecific attentional effects because during the directed attention (dir att; 49/49°C and 49/49°C) pain ratings were greater than during divided attention at distal (49/49°C div att; A) and proximal (49/49°C div att; B) sites.