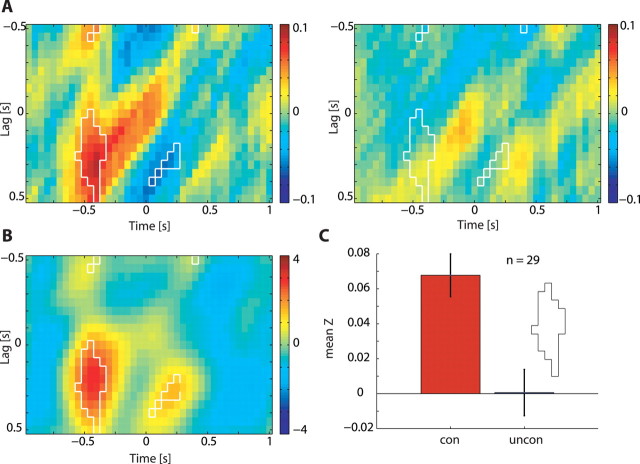
Figure 6.
Comparison of cortico-to-spinal noise correlations between connected and unconnected sites. A, Time-resolved noise cross-correlation averaged across all pairs recorded from functionally connected sites (left, n = 75; monkey D, n = 55; monkey V, n = 20) and functionally unconnected sites (right, n = 88; monkey D, n = 40; monkey V, n = 48). Bins for which correlation values were significantly different between connected and unconnected sites are delineated by a white border. B, Surprise matrix highlights the bins with a significant (p < 0.05) difference between connected and unconnected pairs. There is a significant difference in noise correlation between connected and unconnected sites that appears before torque onset at positive CS lags. C, Bars showing the mean of the z-transformed correlation coefficient in the area of significant difference for functionally connected sites (red) and functionally unconnected sites (blue). The difference between connected sites and unconnected sites is caused exclusively by positive noise correlations found for connected sites, whereas unconnected sites show no noise correlation.