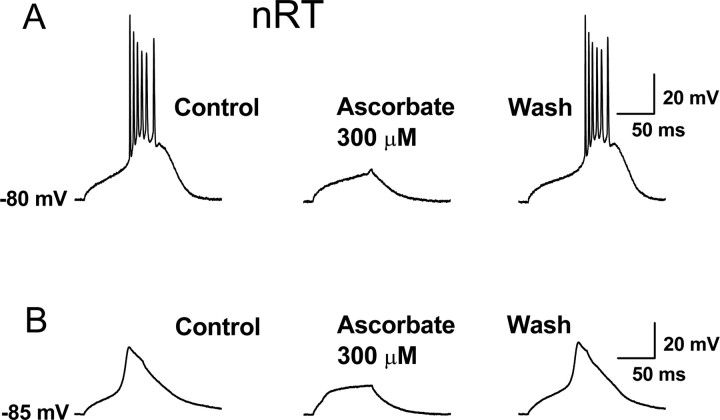
Figure 7.
Ascorbate inhibition of LTSs and burst firing in nRT neurons. A, Representative current-clamp trace from an nRT neuron (the LTS was evoked by a 250 ms, 100 pA current injection at the indicated membrane potential). Application of ascorbate reversibly reduced the amplitude of the LTS and abolished the resulting burst of APs. In similar experiments from five cells, ascorbate reduced the average number of APs crowning the LTS from 4.6 ± 0.7 to 2.4 ± 1.1 (p < 0.01). B, Ascorbate reversibly inhibited the isolated LTS in another nRT neuron. The protocol was similar to that in A, but with the addition of 1 μm TTX to block APs. In similar experiments from six cells, ascorbate reduced the amplitude of the LTS by 44.6 ± 11.4% (p < 0.01).