Figure 10.
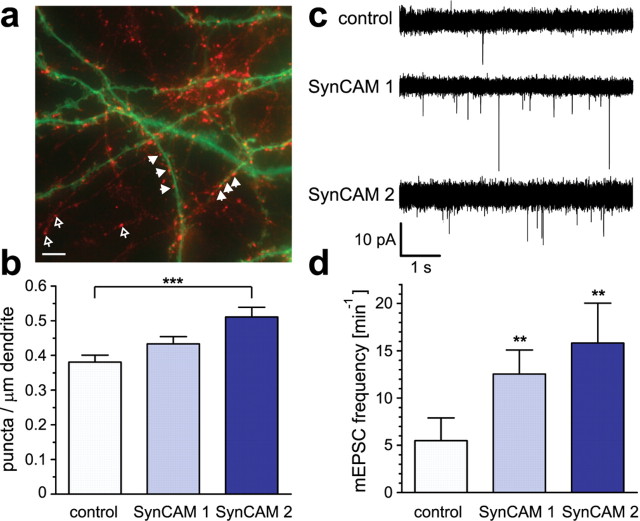
Components of the SynCAM 1/2 complex promote synapse differentiation and synaptic transmission between hippocampal neurons. a, Analysis of postsynaptic SynCAM effects on the formation of presynaptic terminals. Dissociated hippocampal neurons were transfected at 7 d.i.v. with expression vectors for soluble GFP (green) alone or in combination with SynCAM proteins. Four days after transfection, neurons were briefly depolarized, and recycling synaptic vesicles were labeled by uptake of antibodies directed against the luminal domain of synaptotagmin 1 (red). The image shows a neuron coexpressing soluble GFP with SynCAM 1. Filled arrowheads indicate presynaptic terminals containing recycling synaptic vesicles labeled after synaptotagmin 1 uptake (red) found atop dendrites of a transfected neuron (green). Open arrowheads point to presynaptic terminals formed between neighboring untransfected neurons. The cell body of the transfected neuron is to the right and not shown. Scale bar, 5 μm. b, Postsynaptic overexpression of SynCAM 2 promotes formation of presynaptic terminals. The density of synaptotagmin 1 antibody-labeled puncta on proximal dendrites of transfected pyramidal neurons was analyzed after brief depolarization as described in a. Compared with control neurons, postsynaptic SynCAM 1 overexpression caused a 14 ± 7% increase in presynaptic terminal density that was not statistically significant (p = 0.074). SynCAM 2 overexpression resulted in a significant increase of presynaptic terminal density by 34 ± 9% compared with control neurons (p = 0.0002). For image analysis, an average dendrite length of 290 μm was selected per transfected pyramidal neuron starting from the first branch point of proximal dendrites. Results were obtained in independent experiments with neurons expressing only GFP as control (total 13 neurons; 3990 μm dendrite length), with neurons expressing both GFP and SynCAM 1 (14 neurons; 3770 μm dendrite), or with neurons expressing both GFP and SynCAM 2 (12 neurons; 3580 μm dendrite). Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired t tests with two-tailed p values. c, Postsynaptic overexpression of SynCAM 1 and 2 promotes excitatory synaptic transmission of dissociated hippocampal neurons in culture. Five superimposed representative traces show mEPSCs of untreated control neurons and neurons overexpressing SynCAM 1 or SynCAM 2. Coexpression of GFP was used to identify transduced neurons. mEPSC events are recorded at higher frequencies from SynCAM 1 and SynCAM 2 overexpressing neurons than from untransduced control neurons. Expression was performed using the Semliki forest virus system for transduction of neurons. d, SynCAM 1 and SynCAM 2 overexpression significantly increase mEPSC frequencies. Overexpression of SynCAM 1 (n = 14; f = 12.5 ± 2.5 min−1; p = 0.001) and SynCAM 2 (n = 11; f = 15.8 ± 4.2 min−1; p = 0.004) caused a significant increase in mEPSC frequencies compared with untransduced control neurons (n = 19; f = 5.5 ± 2.4 min−1). Expression of GFP alone did not cause a significant difference (data not shown). Statistical analysis was performed using a Mann–Whitney U test with one-tailed p value.