Figure 7.
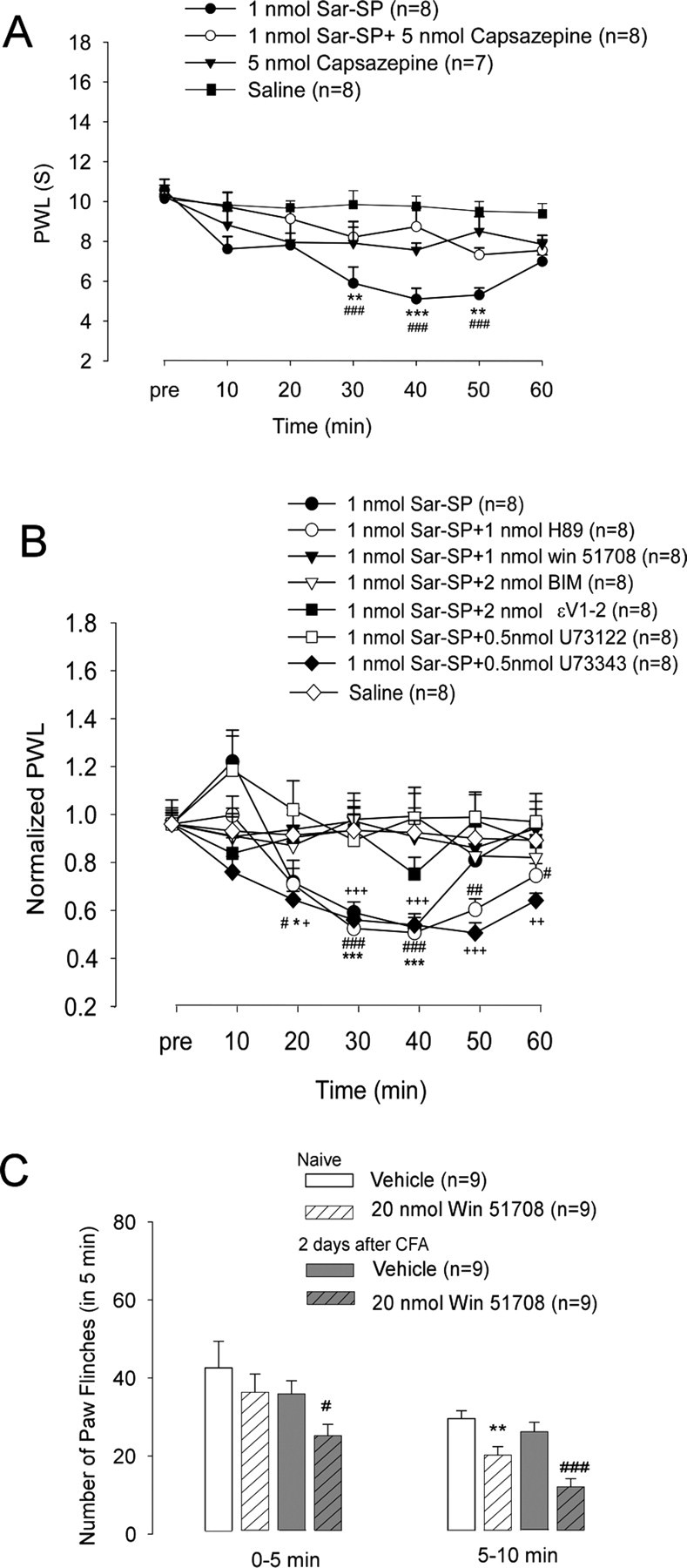
Involvement of peripheral NK-1 activation in thermal hyperalgesia. A, Intraplantar SP-induced thermal hyperalgesia is mediated by TRPV1. Heat hyperalgesia, which was determined by PWL, was induced after intraplantar injection of Sar-SP but not saline. Pretreatment of capsazepine (5 nmol, intraplantar) completely prevented Sar-SP-induced hyperalgesia (###p < 0.001 compared with the saline group; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with the 1 nmol Sar-SP+5 nmol Capsazepine group). Intraplantar capsazepine (5 nmol) did not affect the basal PWL of normal rats. B, Pretreatment by intraplantar administration of NK-1 inhibitor Win 51708 (1 nmol; filled triangles), PKC inhibitor BIM (2 nmol; open triangle), PKCε inhibitor Myr-εv1–2 (2 nmol; filled squares), or U73122 (0.5 nmol; open squares) but not U73343 (inactive control of U73122, 0.5 nmol; filled diamonds) prevented Sar-SP-induced thermal hyperalgesia. Pretreatment of the PKA inhibitor H89 (1 nmol; open circles) failed to prevent the hyperalgesia (filled circles; n = 8). PWLs are expressed as fold of basal level. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Sar-SP injection versus the saline group at each time point. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, Sar-SP+H89 versus saline at each time point (n = 8). +p < 0.05, ++p < 0.01, +++p < 0.001, Sar-SP+U73343 versus Sar-SP+U73122 at each time point (n = 8). Group difference was compared by ANOVA, followed by a post hoc test. C, Effects of peripheral blockade of NK-1 on capsaicin-induced paw flinching in noninflamed and inflamed rats. Two days after CFA injection into the unilateral handpaw, intraplantar injection of capsaicin (0.1%, 10 μl) induced paw flinching, a spontaneous pain, and this spontaneous pain was watched for 10 min, separated by two phases (0–5 and 5–10 min). NK-1 antagonist Win 51708 (20 nmol, intraplantar) was given 10 min before capsaicin injection. Win 51708 reduced the capsaicin-induced second-phase (5–10 min) paw flinching in both inflamed and normal rats. Win 51708 also reduced the first-phase (0–5 min) paw flinching in the inflamed rats. *p < 0.05 versus vehicle of the normal group; #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 versus vehicle of the CFA-inflamed group.
