Figure 6.
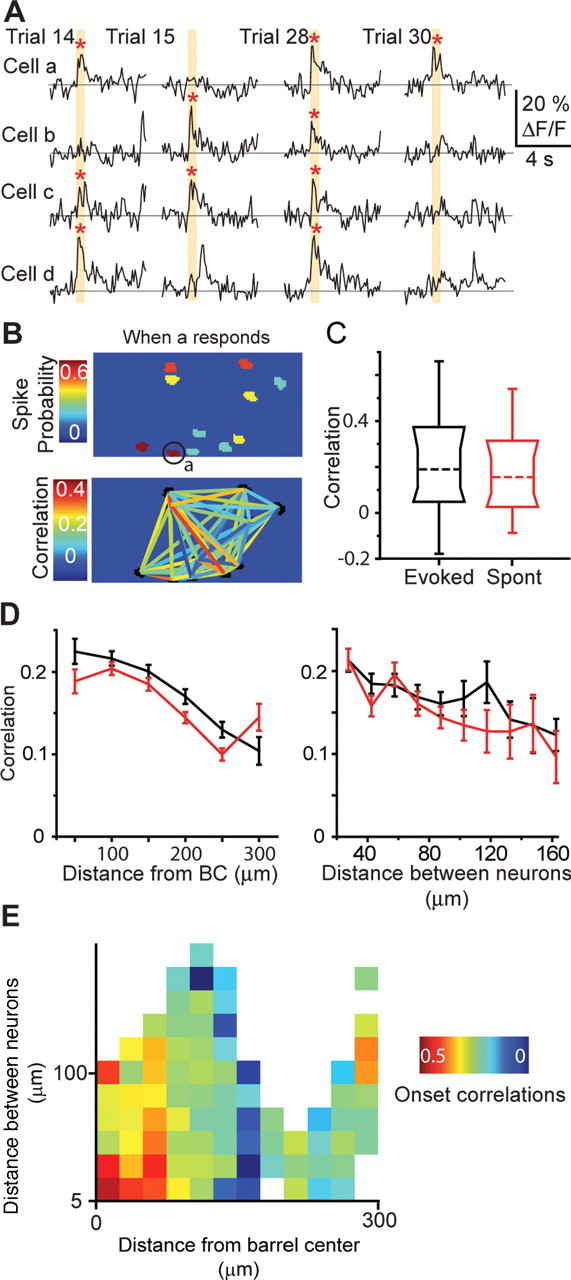
Pairwise correlations depend on location. Whisker deflection increases the correlation between pairs of neurons and is dependent on both distance between neurons and distance from BCC. A, Calcium transients from four simultaneously imaged neurons during four trials of on and off whisker deflection (orange box). Red asterisks represent calcium transients detected as being action potential generated (see Materials and Methods). B, Pseudocolored representation of a population with each neuron colored as a function of correlation when neuron a responds to whisker deflection (top). Correlation between all neurons within the field of view (bottom). C, Comparison of pairwise correlations from evoked and spontaneous (Spont) activity for neurons pooled from all PW related populations. Represented is median (broken line), 10th, 25th, 75th, and 90th percentiles and range. D, Pairwise correlations for both evoked (black) and spontaneous (red) as a function of neuronal pair distance from BCC (left) and distance between neurons (right) for all PW-related neuronal populations. E, Plot of the dependence of pairwise correlations on distance between neurons and on distance from BCC.
