Figure 1.
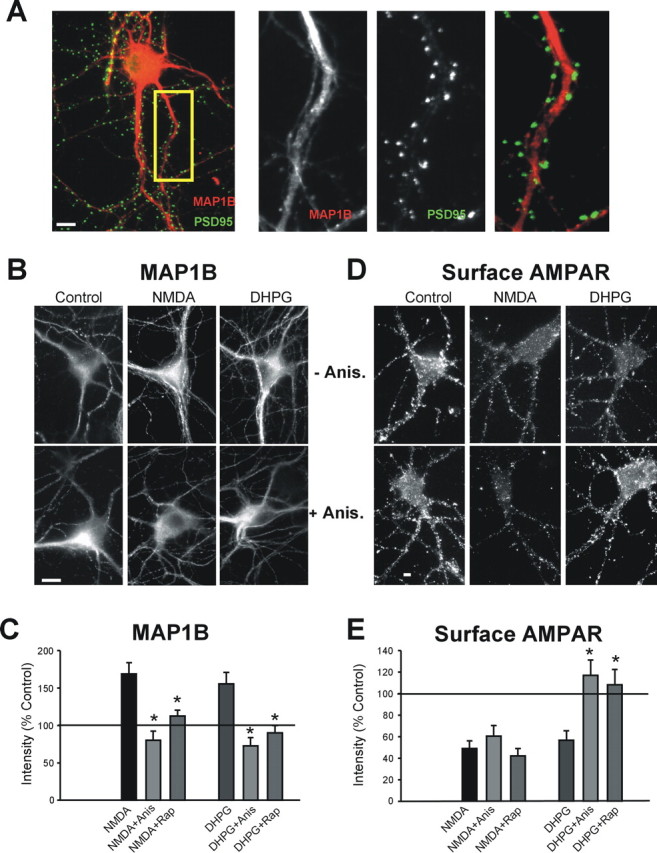
Immunocytochemical expression of MAP1B in dendrites of cultured CA1 pyramidal neurons. A, Colocalization (yellow) between MAP1B (red) and PSD95 (green) in hippocampal neurons. MAP1B, PSD-95, and merged labeling in the inset is enlarged on the right. B–E, NMDA or DHPG treatments, which induce AMPAR endocytosis, increase the dendritic levels and synthesis of MAP1B protein. B, MAP1B immunostaining without and with anisomycin (Anis.) pretreatment in control and DHPG- or NMDA-treated cells. C, Quantitation of MAP1B immunostaining after DHPG in the presence and absence of anisomycin and rapamycin (Rap) (Con, DHPG n = 8; anisomycin n = 5; rapamycin n = 5; *p ≤ 0.05). D, Surface GluR1 immunostaining in neurons labeled live with N-terminal-specific GluR1 antibody in NMDA- or DHPG-treated neurons in the presence or absence of anisomycin. E, Quantitation of surface GluR1 after DHPG treatment in the presence and absence of anisomycin or rapamycin (Con, DHPG n = 8, anisomycin, rapamycin n = 4; *p ≤ 0.05). Scale bars, 10 μm.
