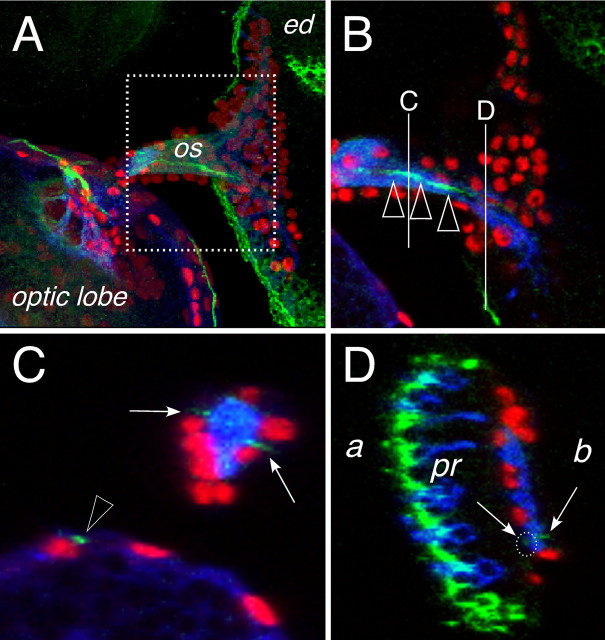
Figure 5.
Subperineurial cells in the eye disc. Confocal images of dissected wild type third larval instar eye imaginal discs. Neuronal membranes are shown in blue (anti-HRP staining), glial cell nuclei are labeled using anti-Repo antibodies (red), NeurexinIV::GFP expression is shown in green. Anterior is to the right. A, Overview of an eye imaginal disc attached through the optic stalk (os) to the brain lobe of a NeurexinIV::GFP-expressing larvae. The dotted area corresponds to the region shown in B. B, Single confocal section, the white lines indicate the positions of the orthogonal sections shown in C and D. The green line of NeurexinIV::GFP expression corresponds to the septate junctions formed by the carpet glia (arrowheads). C, In an orthogonal section through the optic stalk, two regions of NeurexinIV::GFP accumulation can be seen (arrows), similar NeurexinIV::GFP expressing septate junctions are seen in the optic lobe (arrowhead). D, Orthogonal section through the eye imaginal disc. Intense NeurexinIV::GFP staining can be detected on the apical part of the eye disc epithelium (a) next to the photoreceptor cells (pr). Two faint lines of GFP expression can be seen more basal (b) close to the photoreceptor axon tracts (arrows, white dotted circle), which cannot be detected in the frontal view because of the high amount of epithelial NeurexinIV expression.