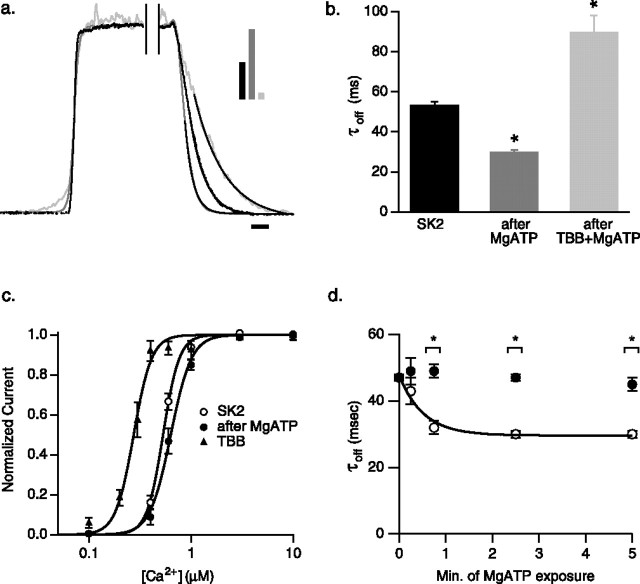
Figure 1.
Activation of CK2 speeds SK2 channel deactivation and reduces the apparent Ca2+ sensitivity. a, Deactivation of normalized SK2 currents after rapid solution exchange from 10 μm to 0 Ca2+; black trace, control (τoff = 57.0 ms); dark gray trace, after a 2.5 min exposure to 5 mm MgATP in 0 Ca2+ (τoff = 29.3 ms); light gray trace, after 2.5 min exposure to 5 mm MgATP in 0 Ca2+ and TBB (τoff = 112.4 ms). Single exponential fits are added to traces. Bars in inset indicate relative current amplitudes. Calibration, 50 ms. b, Average SK2 deactivation time constants derived from single exponential fits for the indicated conditions. c, Normalized steady-state Ca2+ dose–response relationships for SK2 control (open circle), after application of MgATP (closed circle), and additionally in the presence of TBB (triangle). d, Time course of MgATP effect. Separate groups of patches were exposed to 5 mm MgATP for 0 min (n = 10), 0.25 min (n = 11), 0.75 min (n = 12), 2.5 min (n = 11), or 5 min (n = 8) to generate paired, before (black circles) and after (open circles) time points. The time constant of MgATP effect = 0.5 s.