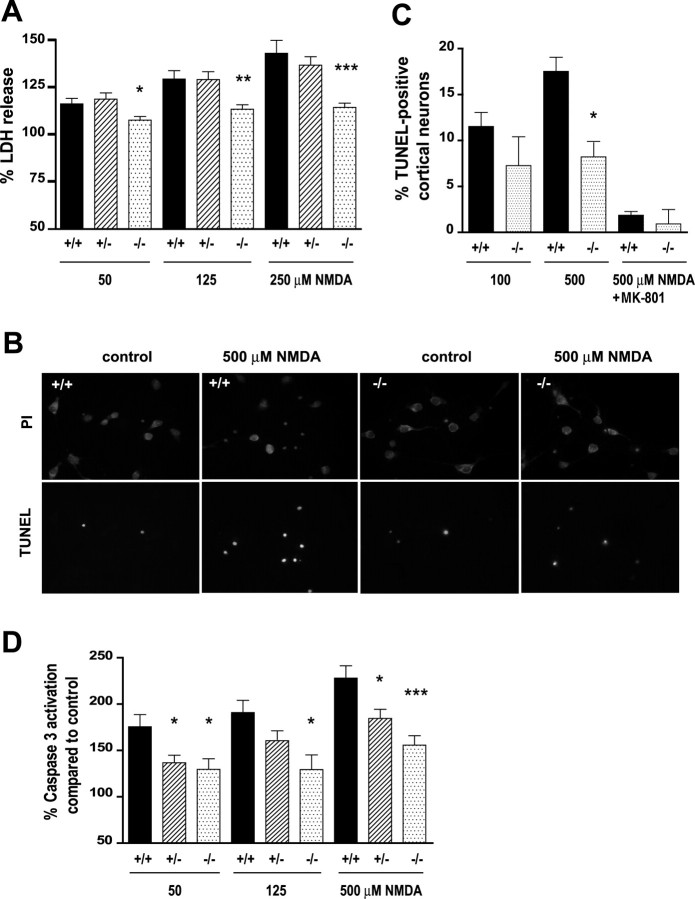
Figure 3.
Reduced NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in HIP1−/− neurons. A, Cortical neurons at 12 DIV were treated with different doses of NMDA and 30 μm glycine for 10 min. After drug removal, neurons were cultured for 14 h, and release of LDH into the cell culture supernatant was measured. Duplicate samples for each condition and genotype in each of six independent experiments were determined. B, Striatal neurons from wild-type and HIP1−/− mice were treated with 500 μm NMDA and 30 μm glycine for 5 min at 9 DIV. After drug removal, neurons were cultured for 20 h and stained for TUNEL-positive neurons (green) followed by PI counterstaining (red). C, Cortical neurons at 12 DIV from wild-type and HIP1−/− mice were treated with 100 or 500 μm NMDA and 30 μm glycine for 5 min in the presence or absence of 50 μm MK-801 and processed as described in B. The number of TUNEL-positive neurons was determined and expressed relative to the number of total neurons. For each sample, 200 neurons were counted for each condition and genotype in each of three independent experiments. D, Cortical neurons at 12 DIV were treated with varying doses of NMDA and 30 μm glycine for 10 min. After drug removal, neurons were cultured for 3 h, and caspase-3 activation was measured fluorometrically by cleavage of Ac-DEVD-AFC. Duplicate samples for each condition and genotype in each of seven independent experiments were determined. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005 compared with wild type; t test. Error bars denote ±SEM.