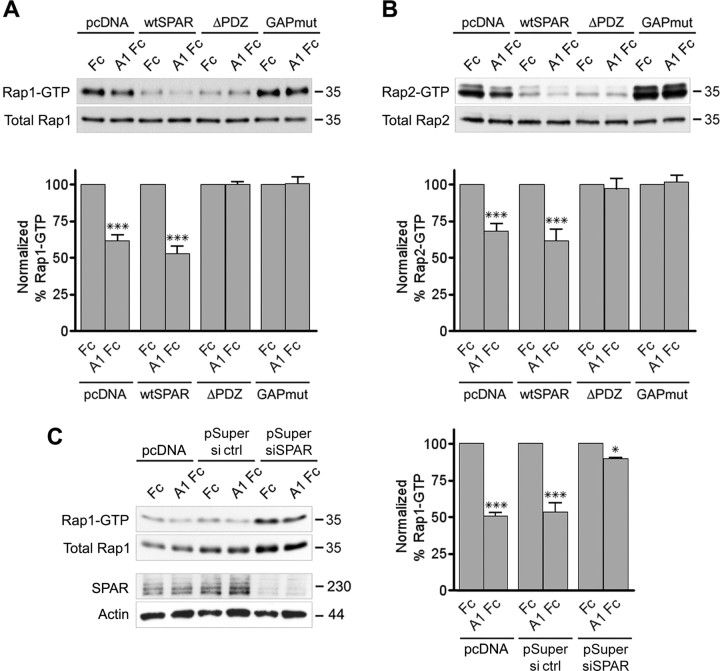
Figure 4.
SPAR mediates ephrin-A-dependent inactivation of Rap1 and Rap2. A–C, HT22 cells were cotransfected with HA-Rap1 (A) or Myc-Rap2 (B) and the indicated SPAR constructs (see Fig. 2B) or HA-Rap1 and pSuper siRNA vector targeting SPAR (pSuper siRNA) or luciferase as a control (pSuper ctrl) (C). The transfected cells were stimulated with preclustered ephrin-A1 Fc (A1 Fc) or Fc control for 8 min. Active Rap1 and Rap2 were isolated by pull-down with GST-RalGDS RBD and detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against the HA or Myc tag. Total HA-Rap1, Myc-Rap2, endogenous SPAR, and β-actin were detected by immunoblotting cell lysates. The levels of each GTP-bound Rap protein were normalized to the corresponding levels of total Rap protein in the lysates. The histograms show the average levels of HA-Rap1-GTP from three experiments and of Myc-Rap2-GTP from five experiments ± SE expressed as a percentage of the levels after Fc treatment of similarly transfected cells. Statistical significance was determined by a two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni posttest. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 for the comparison between ephrin-A1 Fc-treated and Fc-treated.