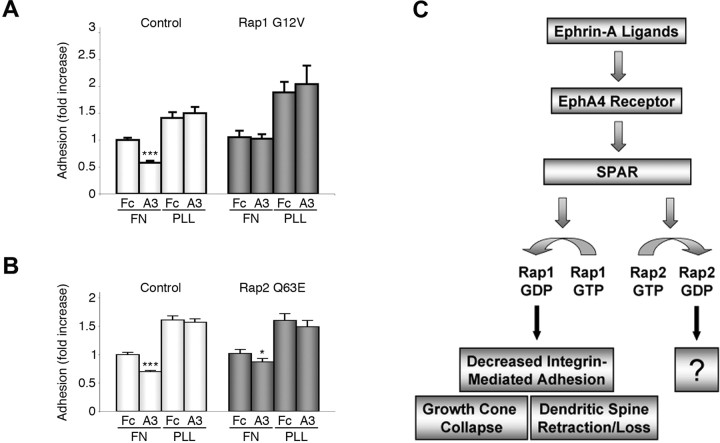
Figure 8.
Constitutively active Rap1 but not Rap2 blocks ephrin-A3-dependent inhibition of integrin-mediated cell attachment. A, B, HT22 cells were transfected with the constitutively active Rap1 G12V (A), Rap2 Q63E (B), or pcDNA3 (control) together with EGFP and plated for 10 min on fibronectin (FN) or poly-l-lysine (PLL). The histograms shows the average percentage of EGFP-positive adherent cells ± SE from four experiments, corrected for transfection efficiency and normalized to control-transfected cells plated on fibronectin and treated with control Fc. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 for the comparison of ephrin-A1 Fc-treated cells with the corresponding Fc-treated cells by two-way ANOVA. C, Schematic illustration of the signaling pathway linking EphA4 receptor stimulation by ephrins in neurons to SPAR-mediated inactivation of Rap GTPases and morphological changes. Rap1 inactivation contributes to ephrin-induced growth cone collapse and loss of integrin-mediated attachment, whereas the effects of Rap2 inactivation downstream of EphA4 remain to be determined.