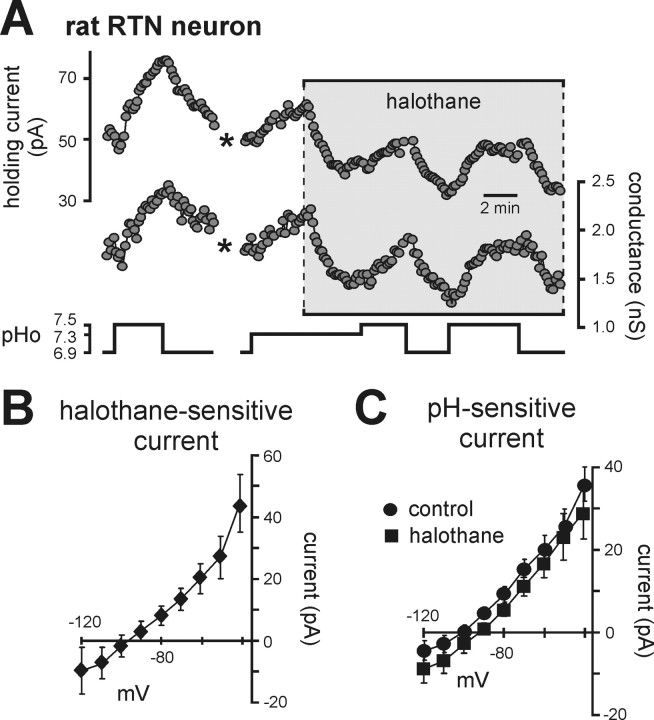
Figure 5.
The pH-sensitive current expressed by rat RTN chemoreceptors is not sensitive to halothane. A, Traces of holding current and conductance in a rat RTN neuron (Vh of −60 mV) during changes in bath pH under control conditions and during exposure to halothane (3%). Note that halothane decreased current and conductance, an effect opposite to that expected for TASK channels, and that effects of pH were similar in magnitude under control conditions and in the presence of halothane. (*, trace blanked and corrected for artifact in recording). B, The I–V relationship of the halothane-sensitive current shows a weakly rectifying profile with a reversal near EK, suggesting inhibition of a background K+ current. C, I–V relationships of pH-sensitive currents under control conditions and in halothane were not different, indicating that TASK channels do not contribute to the pH-sensitive current in rat RTN neurons.