Figure 3.
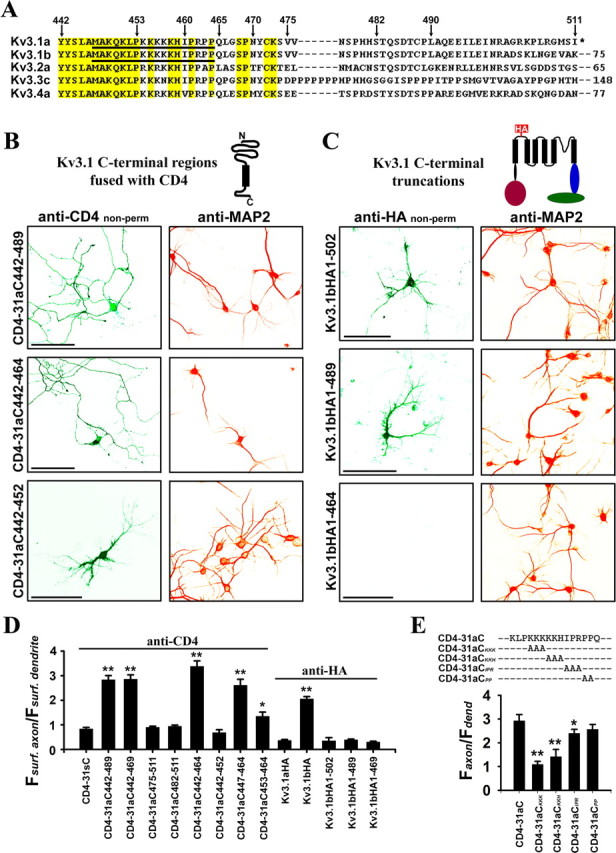
Identification of the axonal targeting motif (ATM) in a highly conserved region of Kv3.1 C terminus. A, Sequence alignment of the C-terminal regions of rat Kv3 channels. Conserved residues are highlighted in yellow. Numbers above the sequence indicate the positions of residues in Kv3.1a. Numbers after the dashed lines indicate the number of extra residues at C-terminal regions. The underlined residues are critical for axonal targeting. Asterisk indicates the end of Kv3.1a C terminus. B, Primarily localized on the axonal surface were CD4–31aC442–489 and CD4–31aC442–464, but not CD4–31aC442–452, which were constructed by fusing different regions from Kv3.1a C terminus (aa 442–489, aa 442–464, and aa 442–452, respectively) to the CD4 C terminus. C, Deleting Kv3.1bHA C-terminal region eliminated axonal membrane targeting. The transfected neurons were first stained with an anti-HA antibody (green) under nonpermeabilized conditions and then permeabilized and stained for the dendritic marker MAP2 (red). Kv3.1bHA1–502 and Kv3.1bHA1–489 became primarily localized on dendritic membranes, whereas Kv3.1bHA1–464 failed to traffic to the plasma membrane. These truncations were generated by engineering a stop codon at positions 503, 490, and 465, respectively. D, Summary of surface targeting of various constructs indicates that the ATM region (M447-Q465) is sufficient to target CD4 to the axonal membrane but fails to target Kv3.1aHA or Kv3.1bHA C-terminal deletions to the axonal membrane. CD4 (in Fig. 2E) and Kv3.1aHA were used as controls in statistics. E, The alanine scan experiment indicates that the lysine-rich motif but not the proline-rich motif is required for axonal targeting. Based on CD4–31aC, three or two consecutive residues were mutated to alanines with the Quickchange mutagenesis strategy. Antibody uptake experiments were performed on neurons expressing these constructs. Here anti-CD4 staining was done under nonpermeabilized conditions. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test. *p < 0.001; **p < 0.0001.
