Figure 4.
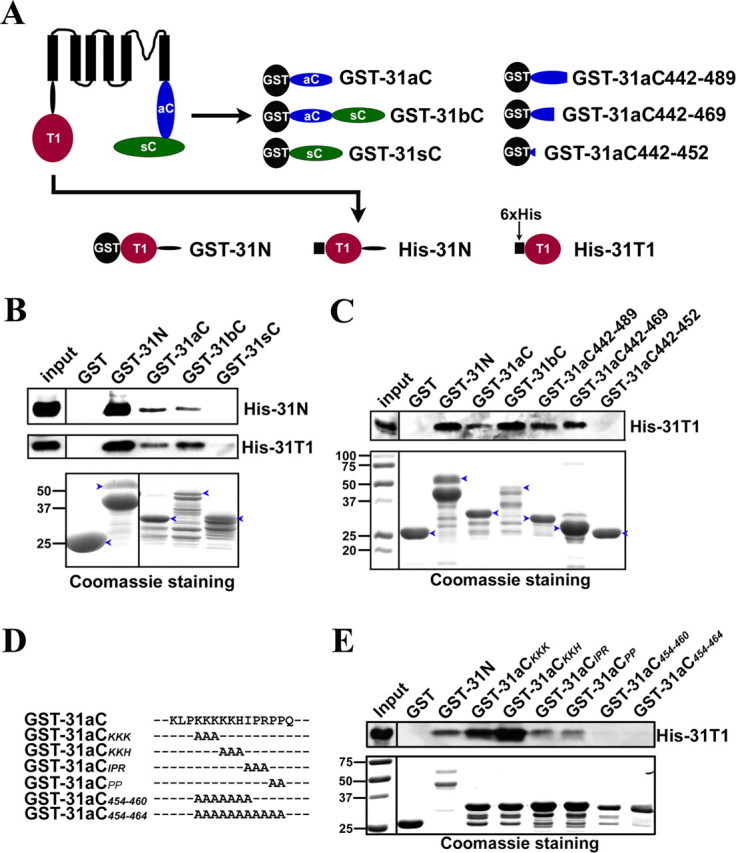
The Kv3.1 T1 domain binds to the C-terminal region. A, Diagrams of Kv3.1b and fusion constructs. Black circles, GST tag. Black squares, 6×His tag. Red circles, The T1 domain. Blue ellipses, The Kv3.1a C-terminal region (31aC). Green ellipses, The Kv3.1b splice domain (31sC). Truncations based on GST-31aC were generated with Quickchange mutagenesis. B, GST-31N, GST-31aC, and GST-31bC, but not GST and GST-31sC, pulled down both His-31N and His-31T1. The bacterial lysates containing a GST fusion protein and a His-tag fusion protein were mixed at a 1:1 ratio in volume and incubated with glutathione agarose beads for 3 h at 4°C. The precipitated proteins were eluted, resolved with SDS-PAGE, and blotted with an anti-His antibody (the top 2 panels). Four percent of the inputs of His-tagged proteins were loaded (left lanes). Fifty percent of the inputs of GST fusion proteins were loaded for Coomassie staining (bottom). C, The ATM precipitated the Kv3.1 T1 domain. GST fusion proteins were expressed in bacteria, purified with glutathione beads, and subsequently incubated on the beads with the bacterial lysates containing expressed His-31T1. The precipitants were blotted with an anti-His antibody (top). GST-31N, GST-31aC, GST-31bC, GST-31aC442–489, and GST-31aC442–469, but not GST and GST-31aC442–452, pulled down His-31T1. D, Sequence alignments of GST-31aC and point mutations in the ATM. E, Residues within the ATM are critical for binding to the T1 domain. Mutating the proline-rich motif but not the lysine-rich motif weakened its binding to the T1 domain, but the binding was completely eliminated only when both motifs were mutated. The experimental procedure here is similar to that in C. The molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons) were at the left lane in the bottom. Blue arrowheads, Full-length GST fusion proteins.
