Figure 9.
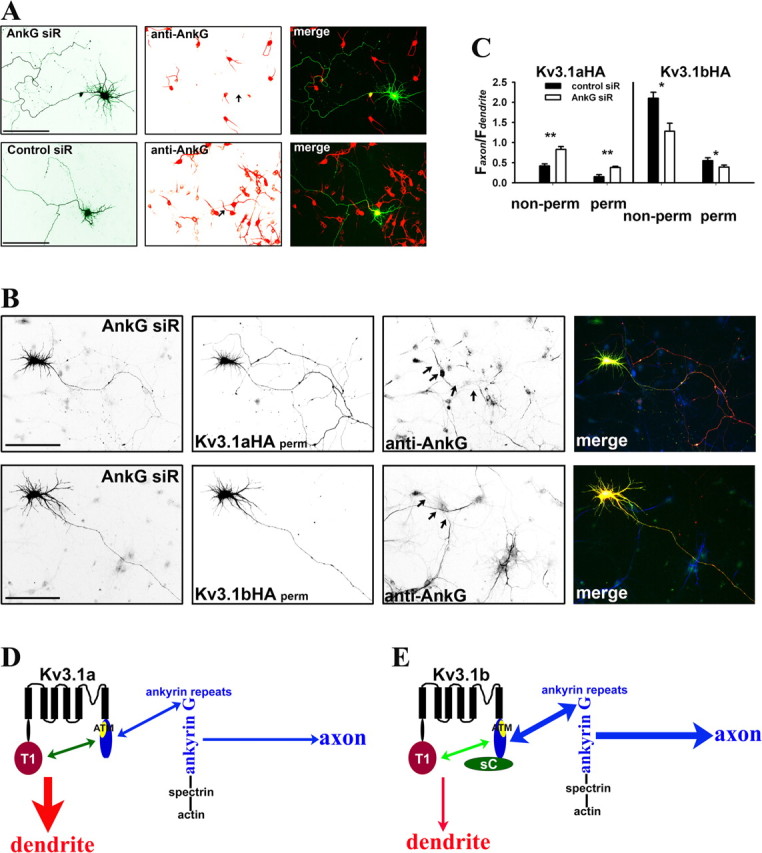
Suppressing endogenous ankyrin G by siRNA altered axon–dendrite targeting of Kv3.1 channels. A, One of four siRNA probes designed against rat ankyrin G, AnkG siR, efficiently suppressed endogenous ankyrin G levels in both soma and axon initial segments. AnkG siR and control probe (Control siR) were transfected into cultured hippocampal neurons at 3 DIV. Five days later (at 8 DIV), the neurons were fixed and stained for endogenous ankyrin G (red). Control siR did not affect ankyrin G levels in both soma and axon initial segments. B, Suppressing endogenous ankyrin G by AnkG siR increased Kv3.1aHA levels in axons and decreased the axon/dendrite ratio of Kv3.1bHA. Neurons were cotransfected with AnkG siR and Kv3.1aHA (top) or Kv3.1bHA (bottom) at 3 DIV and fixed and stained 5 d later. In merged images, AnkG siR is in green, anti-HA staining is in red, and anti-ankyrin G (anti-AnkG) staining is in blue. C, Summary of the effects of siRNA knockdown on Kv3.1 channel targeting. Under nonpermeabilized conditions for anti-HA staining (non-perm), the axon/dendrite ratio of Kv3.1aHA with AnkG siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 0.83 ± 0.07; n = 19) significantly increased compared with that with Control siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 0.42 ± 0.05; n = 20), whereas the axon/dendrite ratio of Kv3.1bHA with AnkG siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 1.28 ± 0.20; n = 13) decreased compared with that with Control siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 2.1 ± 0.15; n = 14). Under permeabilized conditions, the axon/dendrite ratio of Kv3.1aHA with AnkG siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 0.38 ± 0.03; n = 15) also increased compared with that with Control siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 0.15 ± 0.05; n = 15), whereas the axon/dendrite ratio of Kv3.1bHA with AnkG siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 0.39 ± 0.05; n = 18) decreased compared with that with Control siR (Faxon/Fdendrite: 0.55 ± 0.07; n = 18). Arrows, Proximal axons. Scale bars, 100 μm. One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett's test for p values. **p < 0.0001. *p < 0.001. D, E, A model diagram for polarized targeting of Kv3.1 channels. In Kv3.1a (D), the 31T1/31aC interaction masks the ATM to prevent the channel from being accessed by axonal targeting machinery, including ankyrin G. In the axon initial segment, ankyrin G linking various membrane proteins to spectrin/actin cytoskeletons may behave as a trafficking checkpoint. Weak binding between Kv3.1a and ankyrin G does not favor the entry of Kv3.1a to the axon. In Kv3.1b (E), the 31sC domain alters the conformation and/or affinity of the 31T1/31aC interaction, resulting in exposed ATM, which binds to ankyrin G. Thus, Kv3.1b binds to ankyrin G with much higher affinity compared with Kv3.1a, and thereby Kv3.1b is attracted to enter the axon. For simplification, only one subunit of a Kv3.1 channel tetramer is shown here.
