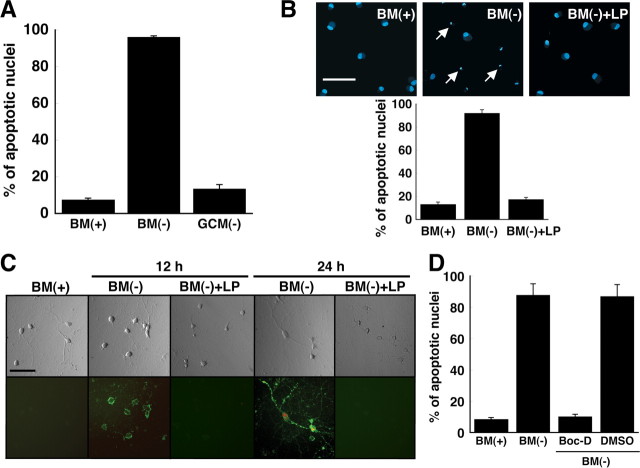
Figure 1.
ApoE-containing glial lipoproteins prevent neuronal apoptosis induced by withdrawal of trophic additives. A, B, Fragmented/shrunken nuclei were detected by Hoechst staining of RGCs after incubation for 24 h in BM(+)] or BM(−). Glia-conditioned medium without trophic additives [GCM(−)] or basal medium without trophic additives but with apoE-containing LPs was added to RGCs. The final cholesterol concentration of LPs in the media was 1 μg/ml. The number of apoptotic neurons was quantified as a percentage of the total number of neurons. Data are means ± SE from five independent experiments. B, Typical images of Hoechst-stained RGCs are shown. Typical apoptotic nuclei are indicated by arrows. C, Shown are phase-contrast (top) and fluorescence (bottom) images of RGCs stained with annexin V–fluorescein (green) and propidium iodide (red) after incubation for 12 and 24 h under the same conditions as for B. Representative images are shown from one of three independent experiments with similar results. Scale bars: B, C, 50 μm. D, Apoptosis induced by withdrawal of trophic additives is inhibited by a broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor. RGCs were incubated for 24 h in BM(+) or BM(−). The medium added to some cultures contained the broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor Boc-D fmk (Boc-D) (100 μm) dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide. Medium provided to control cells (DMSO) contained an equivalent amount (2 μl/ml) of dimethylsulfoxide without inhibitor. Apoptotic neurons were detected by Hoechst staining. Data are means ± SE from four independent experiments.