Figure 4.
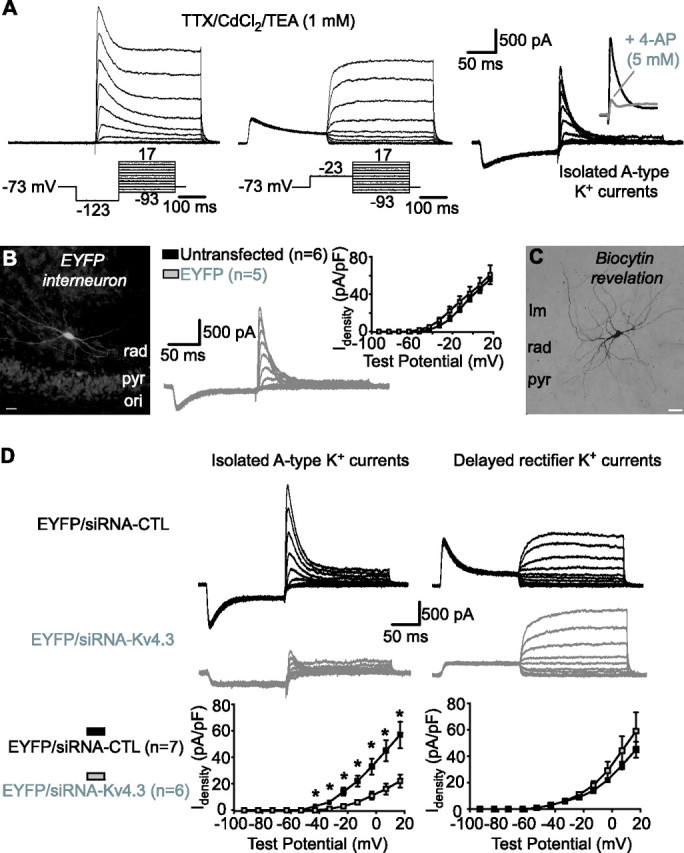
Kv4.3 siRNA reduces A-type K+ currents in interneurons in slice cultures. A, Whole-cell K+ currents recorded from interneurons in TTX (1 μm), CdCl2 (150 μm), and a low concentration of TEA (1 mm). Total K+ currents activated by test pulses from a hyperpolarized potential consisted of rapidly inactivating and delayed components (left). Delayed rectifier K+ currents evoked by test pulses from a depolarized potential (middle) were subtracted to isolate A-type K+ currents (right). Inset shows sensitivity of A-type K+ currents to 5 mm 4-AP. B, Fluorescence image of an EYFP-expressing LM/RAD interneuron (left). Traces from a representative EYFP-expressing interneuron showing isolated A-type K+ currents are shown in the middle. A summary graph illustrating similar A-type K+ current density in untransfected and EYFP-expressing interneurons is shown at the right. C, Example of biocytin labeling of an EYFP-expressing interneuron showing typical nonpyramidal morphology of LM/RAD interneurons. D, Traces from representative interneurons (top) and summary graphs for all cells (bottom), indicating that transfection of Kv4.3 siRNA selectively reduced A-type K+ current density (left) and did not affect delayed rectifier K+ currents (right), compared with transfection with control siRNA. Scale bars: B, C, 25 μm. *p < 0.05.
