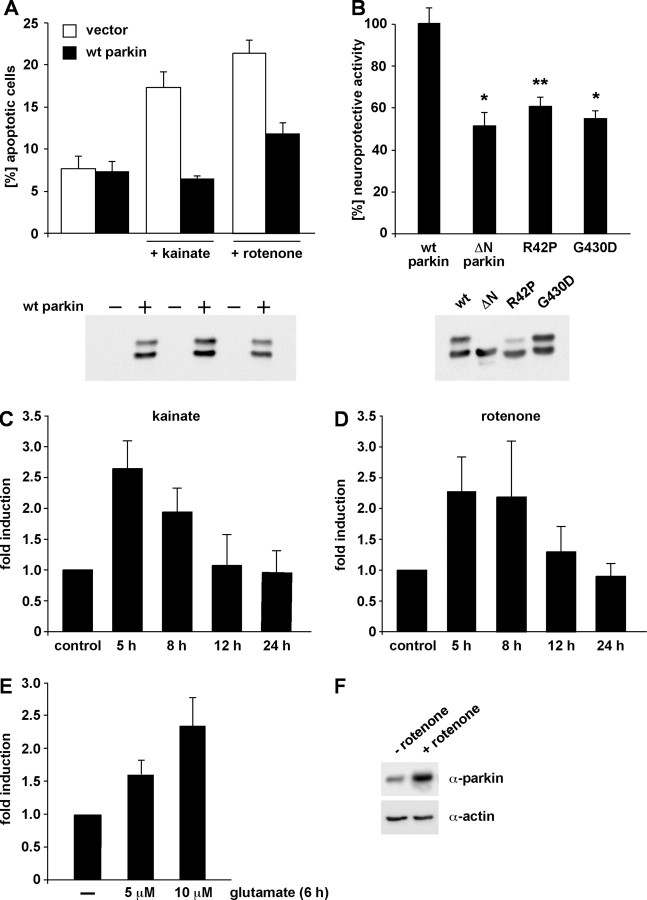
Figure 1.
Parkin is a stress-inducible protein with neuroprotective capacity. A, B, Parkin has a neuroprotective capacity in cultured cells. A, SH-SY5Y cells were cotransfected with EYFP and wt parkin. At 24 h after transfection, cells were incubated with kainate (500 μm) or rotenone (10 μm) at 37°C for 3 h, fixed, permeabilized, and analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence. Activation of caspase-3 was detected using the anti-ACTIVE caspase-3 pAb. Shown is the percentage of apoptotic cells among the transfected cells. B, SH-SY5Y cells were cotransfected with EYFP and either wt parkin or the parkin mutants indicated. At 24 h after transfection, cells were incubated with kainate (500 μm) at 37°C for 3 h and analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence as described in A. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001 compared with cells expressing wt parkin. As a control for parkin expression, an aliquot of the cell lysates was immunoblotted with the anti-parkin pAb hP1 (bottom). C–F, Endogenous parkin is upregulated after cellular stress. SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with 50 μm kainate (C) or 1 μm rotenone (D) for 3 h. Cells were harvested 5, 8, 12, and 24 h after the drug treatment, respectively. Total cellular RNA was isolated and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR using parkin-specific primers. The amount of RNA of each sample was normalized with respect to the endogenous housekeeping control gene β-actin. Shown is the fold increase in the amount of parkin-specific mRNA compared with the untreated control. E, Primary cortical neurons derived from embryonic rat brain were incubated with glutamate (5 or 10 μm) for 6 h and then analyzed as described in C and D. F, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with rotenone (1 μm, 3 h) or mock treated, and expression of endogenous parkin was analyzed by Western blotting using the PRK8 mAb.