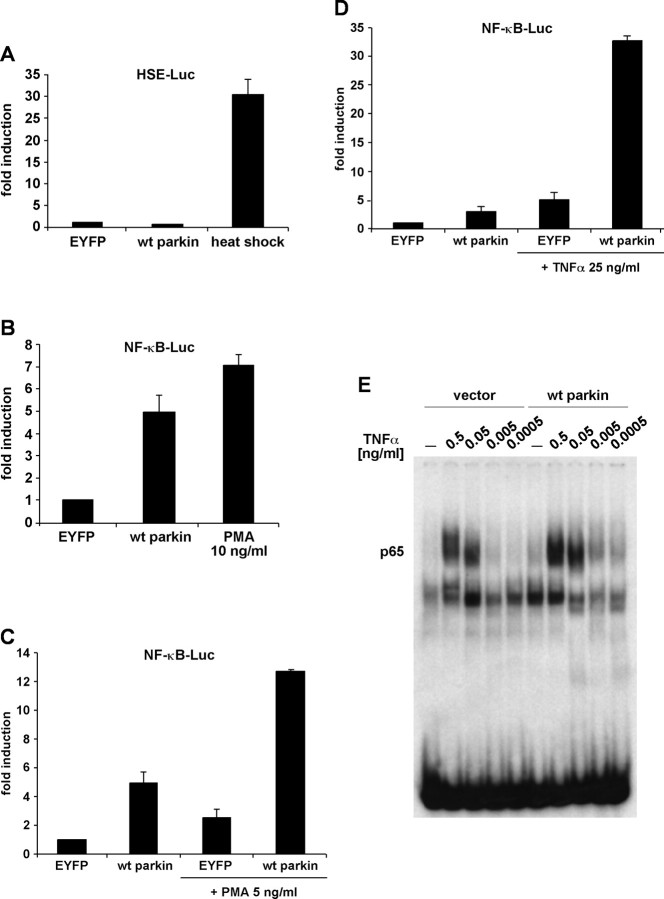
Figure 2.
Parkin stimulates NF-κB-dependent transcription. A, HEK293T cells were cotransfected with a reporter plasmid encoding luciferase under control of an HSF1-inducible promoter (HSE–Luc) and wt parkin. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were subjected to a heat shock (42°C for 15 min), returned to 37°C, and harvested after an additional 16 h. Shown is the fold induction of luciferase activity compared with the EYFP control. B, HEK293T cells were cotransfected with a reporter plasmid encoding luciferase under control of an NF-κB-responsive promoter (NF-κB–Luc) and wt parkin. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were incubated with PMA (10 ng/ml) at 37°C for 3 h and further incubated at 37°C for 16 h. C–E, Parkin sensitizes cells to NF-κB-activating stimuli. C, D, HEK293T cells were cotransfected with NF-κB–Luc and wt parkin. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were incubated with TNFα (25 ng/ml; C) or PMA (5 ng/ml; D) at 37°C and harvested after 7 h. E, HEK293T cells transfected with either wt parkin or vector were incubated with TNFα for 30 min. Nuclear extracts were prepared and probed for NF-κB binding activity by an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. The higher-molecular-weight complex contains p65 as determined by supershift experiments (data not shown).