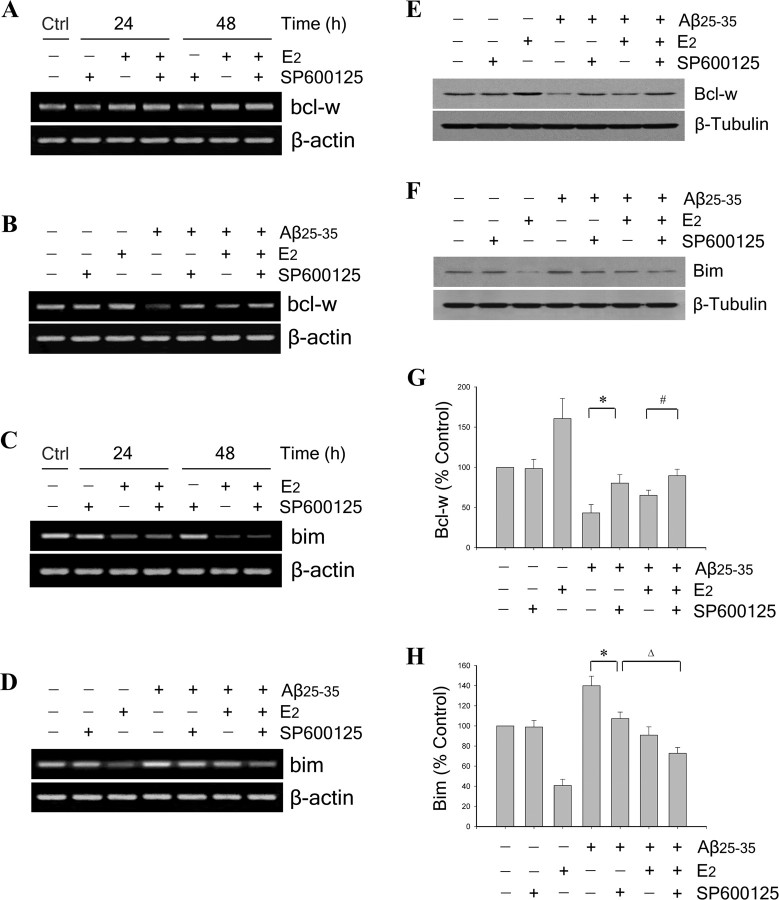
Figure 6.
Estrogen regulation of Bcl-w and Bim expression is JNK independent under basal conditions but involves JNK signaling under Aβ challenge. A, C, Representative agarose gels of RT-PCR products using bcl-w (A) or bim (C) primers show that, under basal conditions, the JNK inhibitor SP600125 neither blocks E2 regulation of bcl-w and bim nor independently affects expression of bcl-w and bim. Neuron cultures were pretreated with 100 nm SP600125 for 60 min, followed by 10 nm E2 for 24 and 48 h. β-actin served as an internal control. B, D, Representative agarose gels of RT-PCR products using bcl-w (B) or bim (D) primers show that the JNK inhibitor SP600125 both independently and additively with E2 blocks Aβ-induced changes in bcl-w and bim expression. Neuron cultures were pretreated with 100 nm SP600125 for 60 min, followed by 10 nm E2 for 60 min, and then exposed to 25 μm Aβ25–35 for 24 and 48 h. β-actin served as an internal control. Effects of JNK inhibition on E2 regulation of bcl-w and bim were extended to protein expression using Western blots. E, F, Representative blots show Bcl-w (E) and Bim (F) and expression in lysates from neuron cultures that were pretreated with 100 nm SP600125, followed 60 min later with 10 nm E2 treatment, and then 60 min later exposed to 25 μm Aβ25–35 for 48 h. G, H, Relative protein levels of Bcl-w (G) and Bim (H) were determined by densitometric scanning of Western blots from three independent experiments. *p < 0.01 relative to Aβ25–35 condition; #p < 0.01 compared with E2 plus Aβ25–35 treatment; Δp < 0.01 relative to Aβ25–35 plus SP600125 condition.