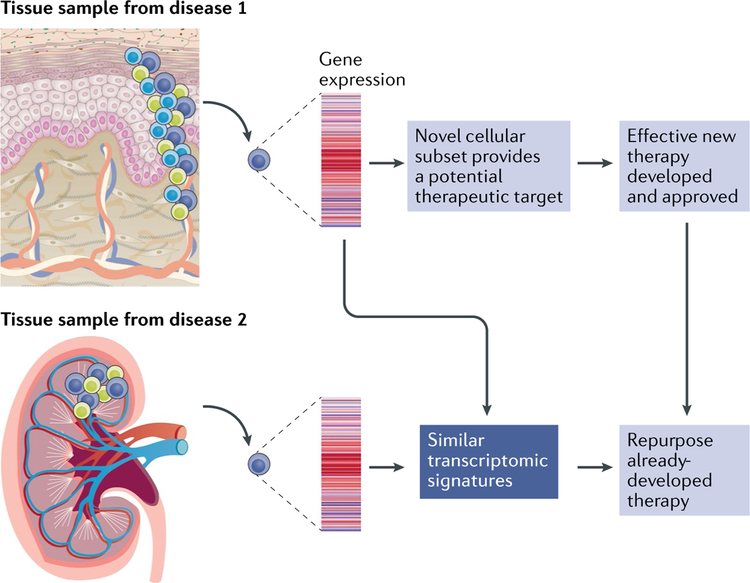
Fig. 2 |. Using transcriptomics to gain insight into rheumatic diseases and develop new therapeutics.
Single-cell transcriptomic techniques have already provided initial findings of novel cell types and activation states in tissues affected by rheumatic diseases. Further advances could include identification of an immune cell that might share a similar transcriptomic profile in distinct tissues and diseases, such as the kidney in lupus nephritis and the skin in systemic sclerosis, thereby providing support for evidence-based therapeutic targeting of the same pathway in distinct clinical conditions. Linking these findings with the most appropriate therapeutics will be the important next step, which could involve repurposing medications developed for other diseases that share similar molecular transcriptomic patterns.