Figure 3.
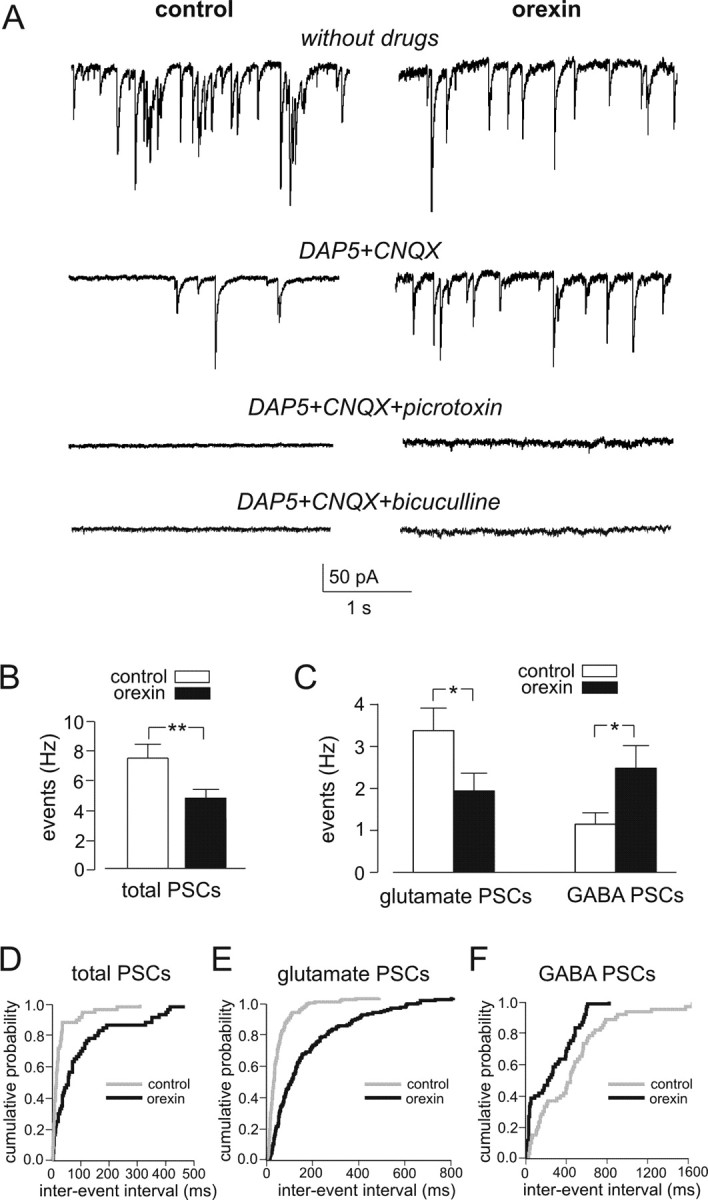
Effects of orexin on spontaneous glutametergic and GABAergic inputs. A, Representative recordings of PSCs at −60 mV before (left, control) and after (right, orexin) the addition of 100 nm orexin to the external solution. Top traces, No additions. Middle traces, In the presence of 50 μm d-AP-5 plus 10 μm CNQX. Bottom traces, In the presence of 100 μm picrotoxin (or 20 μm bicuculline) plus 50 μm d-AP-5 plus 10 μm CNQX. B, Mean PSC frequency before and after exposure to 100 nm orexin. **p < 0.01. C, Mean glutamatergic and GABAergic PSC frequency before and after exposure to 100 nm orexin. *p < 0.05. Glutamate PSCs were identified by their sensitivity to d-AP-5/CNQX and GABA PSCs by sensitivity to picrotoxin. D–F, Cumulative probability distributions of inter-PSC intervals, showing that orexin significantly increases the intervals between total (D) and glutamergic (E) PSCs but reduces the intervals between GABAergic PSCs (F). Glutamergic PSCs (E) were recorded in the presence of 20 μm bicuculline and 100 μm CGP 35348. Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests indicated significant differences between orexin and control PSC distributions: p < 0.001, k = 0.48 (D); p < 0.001, k = 0.49 (E); p < 0.01, k = 0.3 (F). Data from at least three cells (and >50 intervals per cell) were used for each graph.
