Figure 3.
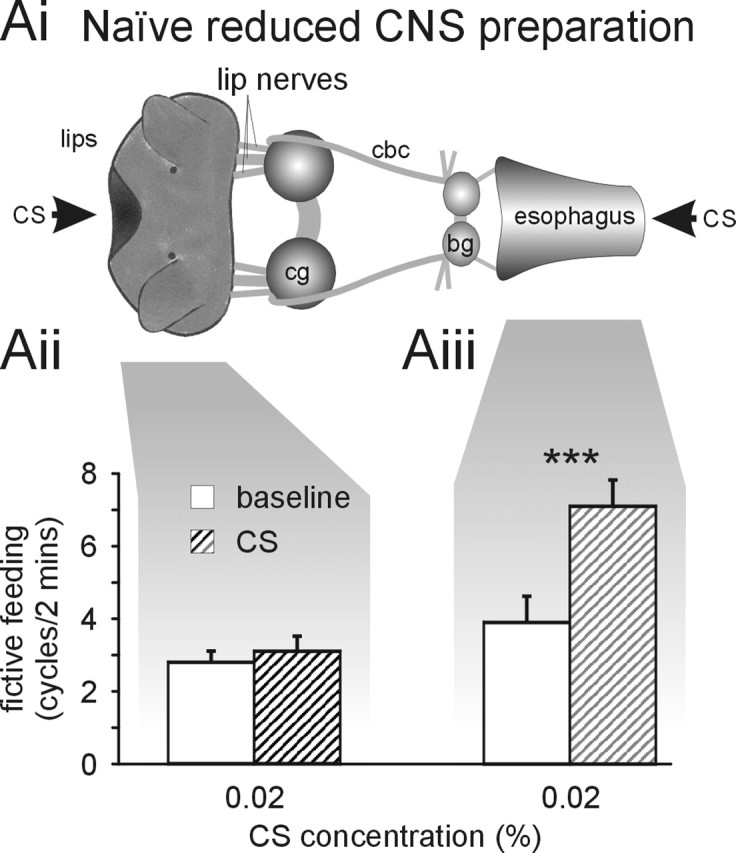
Inhibitory effect of CS application to the lips requires whole CNS. Ai, Schematic diagram of reduced CNS semi-intact preparation. The reduced CNS preparation is similar to the semi-intact preparation shown in Figure 1 but lacks all central ganglia apart from the cerebral ganglia (cg) and the buccal ganglia (bg). This left direct lip–cerebral–buccal and esophageal–buccal pathways intact but removed all indirect pathways requiring neuronal elements outside the cerebral–buccal ganglia. cbc, Cerebral buccal connectives. Aii, CS application (0.02%) to the lips of reduced semi-intact preparations does not significantly alter fictive feeding activity during the 2 min application (CS) compared with the 2 min before stimulus application (baseline). Aiii, CS application (0.02%) to the esophagus of reduced CNS preparations causes a highly significant increase in baseline fictive feeding activity by 3.2 ± 0.4 cycles/2 min (paired t test, p < 0.001; n=10), which is similar to the feeding stimulatory effect of 0.02% CS application in the whole CNS preparation (3.9 ± 0.7 cycles/2 min; n=7; t test, p > 0.05). ***p < 0.001.
