Figure 2.
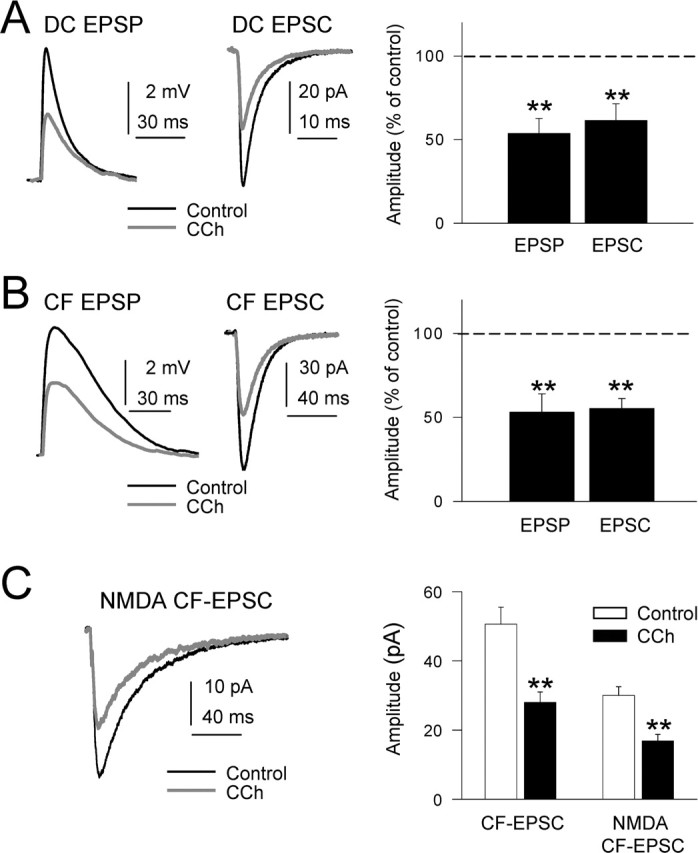
Inhibition of DC-EPSPs and -EPSCs by CCh. A, Left, Superimposed DC-EPSPs recorded in current-clamp conditions in control ACSF (black trace) and with 10 μm CCh (gray trace). During CCh, the Vm was adjusted at the resting value (−65 mV) by continuous current injection. A, Middle, Same as A, left, but EPSCs recorded in voltage-clamp conditions at −65 mV holding potential. A, Right, Summary data showing the inhibition of DC-EPSP and -EPSC by CCh (n = 27; p < 0.01 in both cases). B, Left and right, Same as A, left and right, but for CF-EPSPs and -EPSCs. C, Left, Superimposed isolated NMDA EPSCs (Mg2+-free ACSF plus 20 μm CNQX; black trace) and when CCh was added (gray trace). C, Right, Summary data showing the inhibition of CF-EPSP and isolated NMDA CF-EPSC by CCh (n = 7; p < 0.01).
