Figure 6.
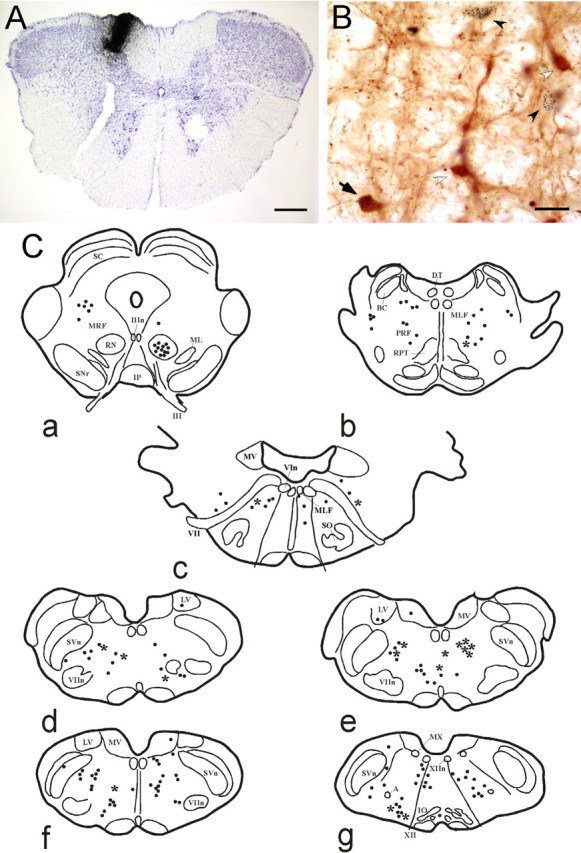
Origin of cholinergic afferents to the GN. A, Microphotograph of a medullary coronal section showing a CTb injection (i.e., CTb staining) in the gracile nucleus. Scale bar, 450 μm. B, Samples of ChAT (white arrowhead), CTb-positive (black arrowhead), and double-labeled (arrow) neurons in the gigantocellular bulbar reticular nucleus. Scale bar, 40 μm. C, Schematic drawings of coronal sections from rostral (a) to caudal (g) of the rat brain in one of our cases, showing the distribution of CTb-positive neurons (dots) and double-labeled neurons (asterisk). A, Ambiguous nucleus; BC, brachium conjunctivum; DT, dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden; IO, inferior olive; Ip, interpeduncular nucleus; LV, lateral vestibular nucleus; ML, medial lemniscus; MLF, medial longitudinal fascicle; MRF, mesencephalic reticular formation; MV, medial vestibular nucleus; MX, motor nucleus of the vagus nerve; PRF, pontine reticular formation; RN, red nucleus; RPT, pontine reticular nucleus; SC, superior colliculus; SNr, sustantia nigra pars reticulata; SO, superior olive; SVn, spinal trigeminal nucleus; III, oculomotor nerve; IIIn, nucleus of the oculomotor nerve; VIn, nucleus of the abducens nerve; VII, facial nerve; VIIn, nucleus of the facial nerve; XII, hypoglossal nerve; XIIn, nucleus of the hypoglossal nerve.
