Figure 2.
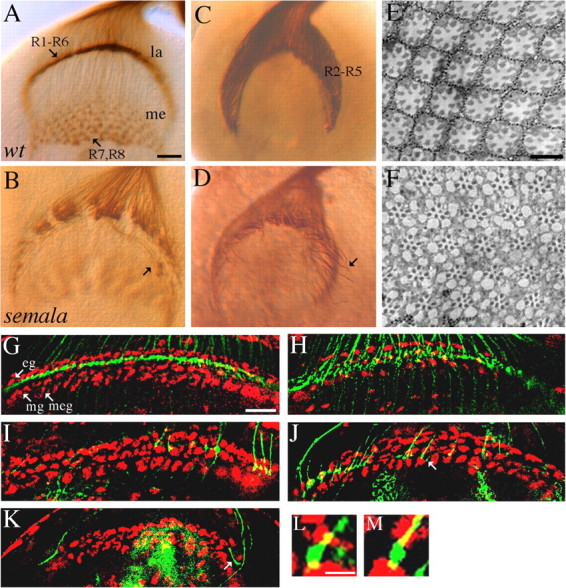
semala is specifically required for the establishment of an appropriate local retinotopic termination pattern. A, B, Third-instar larval eye–brain complexes were stained with MAb 24B10 to visualize all R-cell axons. In wild type (wt; A), expanded R1–R6 growth cones associate closely with each other and elaborate a smooth and dense terminal layer in the lamina (la). R7 and R8 axons project through the lamina into the medulla (me). In a sema1aP1 homozygote (B), R1–R6 growth cones associated loosely with neighboring growth cones. Some R1–R6 axons migrated laterally at the bottom of lamina into incorrect topographic locations (B, arrow). C, D, R2–R5 axons in wild type (C) and sema1aP1 homozygous mutants (D) were labeled with the ro-τ-lacZ marker. Like that in wild type (C), the vast majority of mutant R2–R5 axons still terminated in the lamina (D). Note that some R2-R5 axons (arrow) migrated abnormally at the bottom of lamina (D). E, F, Wild-type (E) and sema1aP1 mosaic (F) adult eyes were embedded in Epon and sectioned. G, H, R-cell axons (green) and glial nuclei (red) in wild-type (G) and sema1aP1 mosaic (H) third-instar larval brains were double-stained with MAb 24B10 and anti-Repo, respectively. In wild type (G), R1–R6 growth cones terminate in between epithelial (eg) and marginal (mg) glial layers. In a sema1aP1 mosaic individual (H) in which large clones of homozygous mutant eye tissues were generated (Newsome et al., 2000), R1–R6 growth cones were distributed in a much broader area between the lamina glial and the medulla glial cells (meg). I–K, Single wild-type (I) or sema1a mutant (J, K) axons were positively labeled. sema1a single-mutant axons frequently passed over the marginal glial layer (J, arrow). Note the three-layered glial structure at the edge of lamina termination site was distorted as a result of mounting. Axons at these regions were not included when the phenotype of stopping at incorrect glial layers was quantitated. Some (K, arrow) terminated at incorrect topographic locations. L, M, High-resolution view of expanded wild-type (L) and sema1aP1 mutant (M) R-cell growth cones (green) surrounded by glial cells (red) at lamina termination site. Scale bars: (in A) A–D, 20 μm; (in E) E, F, 10 μm; (in G) G–K, 20 mm; (in L) L, M, 4 μm.
