Figure 8.
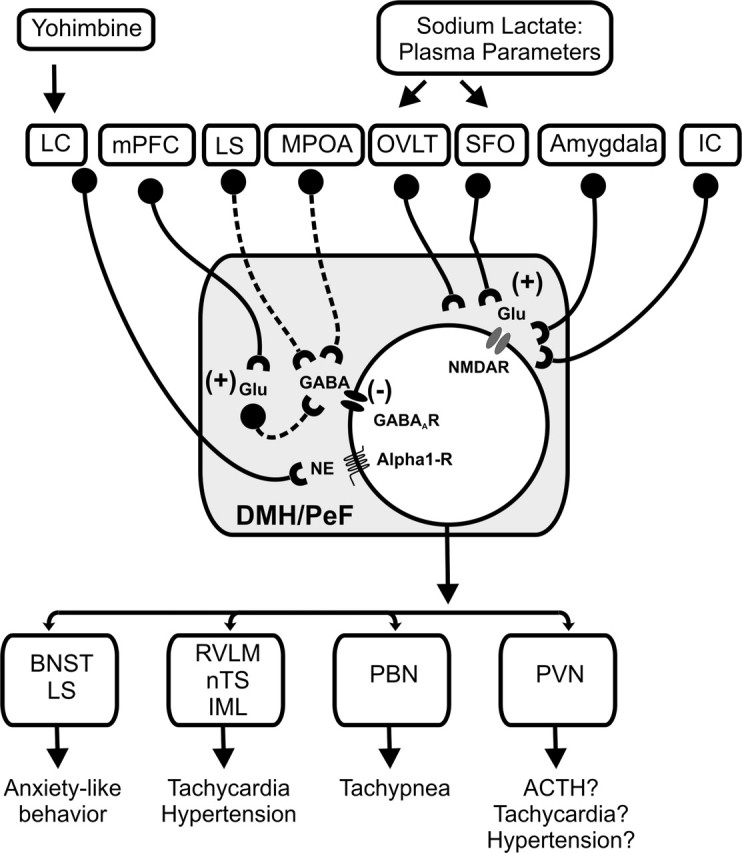
Summary schema of glutamatergic (Glu) and GABAergic input into the DMH/PeF and important efferent brain regions implicated in the regulation of panic-like responses. GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons are represented by circles attached to dashed or solid lines, respectively. Sources of GABA include local interneurons as well as efferent brain regions such as the lateral septum (LS) and medial preoptic area (mPOA) (Feldblum et al., 1993; Risold and Swanson, 1997; Thompson and Swanson, 1998; Herman et al., 2003). This GABAergic input appears to inhibit the DMH tonically, because inhibiting the mPOA increases cellular activity in the DMH (Satoh et al., 2004) and exaggerates cardioexcitatory responses in l-AG plus lactate-treated rats (Shekhar and Keim, 1997); injections of l-AG into the LS also make rats prone to having panic-like physiological responses to intravenous infusions of 0.5 m sodium lactate (S. Keim and A. Shekhar, unpublished observations). Another well known regulatory afferent of the hypothalamus is the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) (Bard, 1928; Bard and Mountcastle, 1948), which innervates the DMH (Vertes, 2004) and appears to inhibit the DMH tonically (Bard, 1928; Bard and Mountcastle, 1948; McDougall et al., 2004), presumably via glutamatergic projections onto local GABAergic interneurons in the DMH, as is the case in the amygdala (Quirk et al., 2003). Glutamatergic input that excites the DMH/PeF region appears to arise from afferent sites such as the CVOs [i.e., OVLT and subfornical organ (SFO) (Richard and Bourque, 1992; Grob et al., 2003)], the amygdala (Soltis et al., 1998), and also the insular cortex (IC) (Cechetto and Chen, 1990; Butcher and Cechetto, 1998). Furthermore, systemic injections of yohimbine, which provokes panic attacks in many panic disorder patients, may induce panic-like responses via brain regions such as the DMH, because exposure to stress (Lowry et al., 2003) and fearful stimuli (Shekhar et al., 1994) increases norepinephrine (NE) concentrations in the DMH, and injecting α1-blockers into the DMH of panic-prone rats before yohimbine infusions blocks panic-like responses (Shekhar, unpublished observations). Afferent targets of the DMH that are implicated in the regulation of panic-like responses are listed also (Chamberlin and Saper, 1994; Thompson and Swanson, 1998; Fontes et al., 2001; Chen et al., 2004). BNST, Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; IML, intermediolateral cell column of spinal cord; LC, locus ceruleus; nTS, nucleus of solitary tract; PBN, parabrachial nucleus; PVN, paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus; RVLM, rostroventrolateral medulla.
