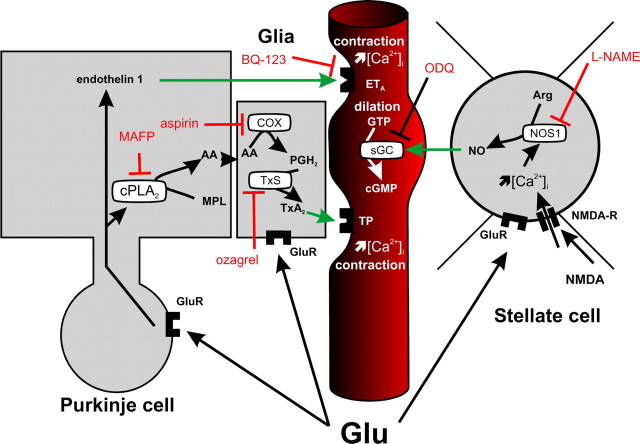
Figure 7.
Hypothetic representation of the glutamatergic modulation of neurovascular coupling in the cerebellum. Activation of NMDA receptors (NMDA-R) on stellate cells by glutamate (Glu) induces NO synthesis and release (inhibited by L-NAME) and subsequent vasodilation of neighboring blood vessels through activation of sGC (inhibited by ODQ). In contrast, activation of glutamate receptors (GluR) on Purkinje cells induces endothelin 1 and arachidonic acid (AA) release from membrane phospholipids (MPL). Endothelin 1-induced vasoconstriction is blocked by the selective ETA receptor antagonist BQ-123. In glia, arachidonic acid is successively metabolized into prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) by cyclooxygenase (COX; inhibited by aspirin) and into thomboxane A2 (TxA2) by thomboxane synthase (TxS; inhibited by ozagrel). Release of TxA2 constricts neighboring blood vessels via thromboxane A2 receptors (TP). Although some of these pathways can also occur in Purkinje cells, they were omitted from the figure for clarity. Arg, Arginin.