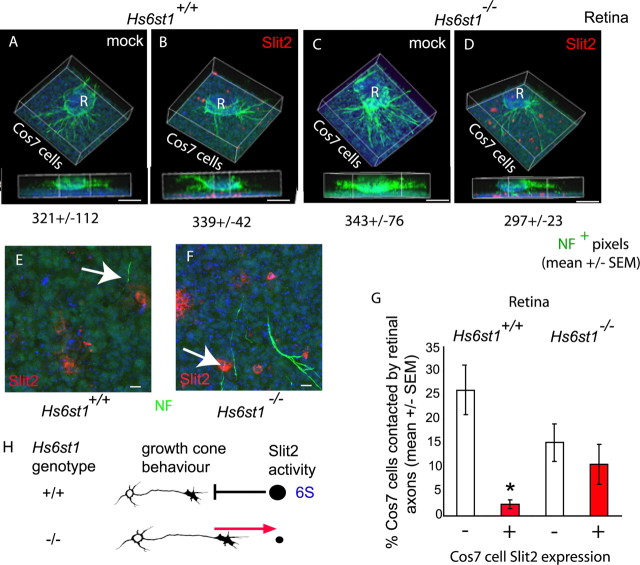
Figure 9.
Hs6st1 is required for Slit2 avoidance by RGC axons. A–D, Collagen cultures of E14.5 Hs6st1+/+ (A, B) or Hs6st1−/− (C, D) retinal explants (R) over a bed of Cos7 cell suspension (Cos7 cells) transfected with the empty vector mock (A, C) or the hSlit2-cmyc-expressing vector Slit2 (B, D). RGC axons are immunostained for neurofilament (NF) protein (green), and hSlit2-cmyc is immunostained for cmyc (red). Nuclei are stained blue with TOPRO3. In each case, a 3D reconstruction of the culture is shown as an elevated perspective and as a side view. Neurofilament+ pixel counts (mean ± SEM) are given below each image, showing that total RGC axon outgrowth is similar under all four culture conditions. E, F, Higher magnification of the Cos7 cell layer viewed from above. E, Hs6st1+/+ RGC axons tend to avoid Slit2+ cells (the arrow points to an RGC axon that has veered away from a Slit2+ cell). F, Hs6st1−/− RGC axons frequently grow over Slit2+ Cos7 cells (the arrow points to an example). G, Histogram comparing the percentage of hSlit2-cmyc+ (red bars) and hSlit2-cmyc− (white bars) Cos7 cells contacted by Hs6st1+/+ and Hs6st1−/− RGC axons (see Results for full description of assay). The asterisk indicates a significant difference (Mann–Whitney rank–sum test, p < 0.05). H, Summary of the role of Hs6st1 in Slit2-mediated axon guidance based on these in vitro observations. The amount of Slit repulsion experienced by growth cones of each genotype is indicated by the size of the black circle. 6-O sulfated heparan (6S) allows Slit2 to exert its repulsive activity on RGC growth cones. In the absence of 6S, RGC growth cones no longer take evasive action when encountering a source of Slit2. Scale bars: A–D, 200 μm; E, F, 10 μm.