Figure 9.
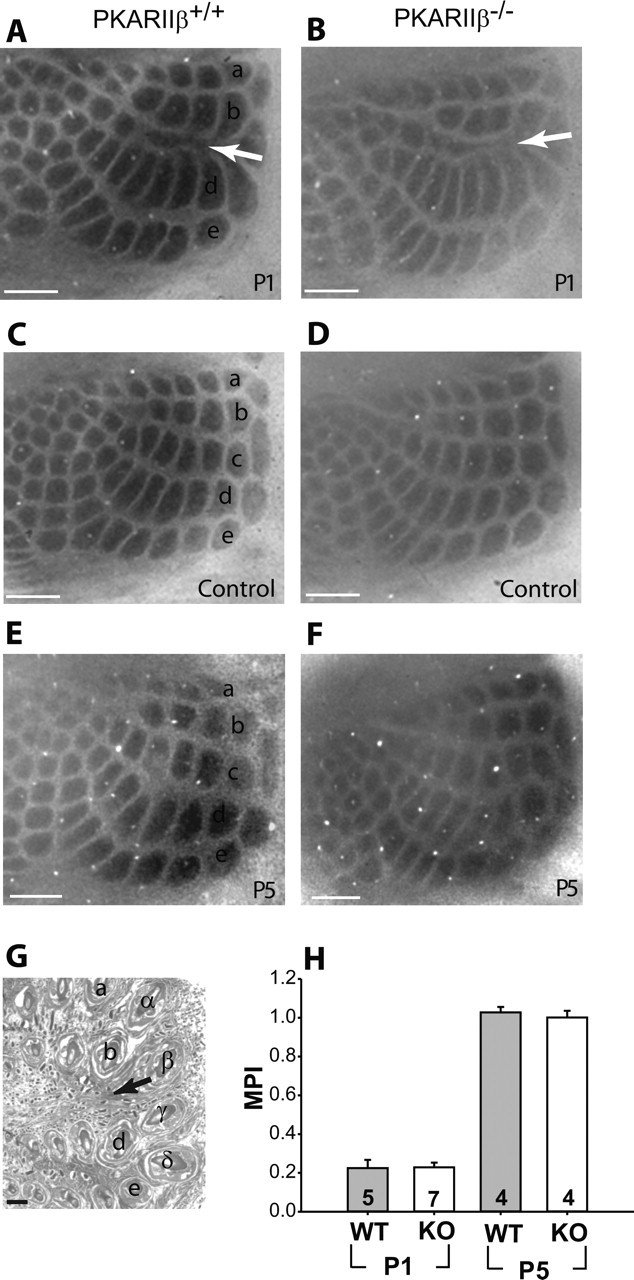
TCA barrel map plasticity is normal in PKARIIβ−/− mice. A, B, CO staining of tangential sections from barrel cortex shows that C-row whisker cauterization at P1 induced robust map plasticity in TCAs of both PKARIIβ−/− mice (B) and their littermate controls (A). C, D, Barrel cortex of control hemispheres where corresponding whiskers were left intact show a normal barrel pattern. E, F, Map plasticity critical period ends by P5 for both PKARIIβ−/− (F) and wild-type control mice (E). G, H&E staining of the cauterized whisker pad confirms that the cauterizations were limited to the C row of whiskers. H, Summary quantification of barrel map plasticity measured with an MPI (see Materials and Methods). CO barrel map plasticity is significant for wild-type littermate control and PKARIIβ−/− (KO) mice at P1 (p ≪ 0.001; t test) compared with control hemispheres (data not shown). However, comparison of MPIs for PKARIIβ−/− mice and wild-type (WT) littermate controls show no significant difference neither at P1 (p = 0.93; t test) nor at P5 (p = 0.57; t test). Scale bars, 500 μm. Error bars indicate SEM.
