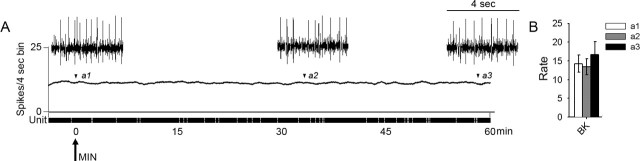
Figure 5.
Spontaneous background activity of lumbar dorsal horn multireceptive units was recorded in SCI animals 30 d after injury, after acute spinal administration of minocycline (A, arrow). Minocycline had no effect on ongoing activity over the course of 60 min. Expansion of waveform traces is shown for periods corresponding to time of minocycline administration (a1), peak effectiveness of drug (a2) (Fig. 4), and at the end of 60 min (a3). Quantification (B) of mean spontaneous firing revealed no significant differences at any point in response to minocycline (bin width, 4 s). Error bars represent mean ± SD. BK, Background.